All Departments
- Aortic valve stenosis (Aortic stenosis)
- arteriovenous malformations
- Avascular Necrosis
- Best cosmetic dentistry in Iran| Dental Treatment in Iran
- Breast Augmentation in Iran|Breast implant in iran
- Breast Reduction surgery
- Cancer in Iran: oncology in Iran
- Cardiology
- Cataract surgery in Iran
- Cochlear Implant Surgery in Iran
- Cosmetic Laser
- Cosmetic Surgery
- Ear cosmetic surgery
- Eye Care
- Eyelid surgery (Blepharoplasty)
- General Heart Surgery in Iran
- General surgery in Iran
- Glaucoma Treatment In Iran
- Hair Transplant
- Heart valve surgery
- lasik Eye Surgery
- Liposuction
- Non-Surgical Cosmetic procedures in iran
- Organ Transplantation in Iran
- Orthopedic
- Paget disease of bone
- Pediatrics
- Plastic surgery
- Psychiatry
- Radiology
- Rhinoplasty surgery in iran
- Shoulder Replacement Surgery
- SkinCare Treatment
- Spinal cord injury
- urolithiasis procedure in iran
- Urology
- Varicocelectomy
Opening Hours

Urology
Iran is a compelling choice for urology due to its renowned medical expertise and advanced healthcare infrastructure. Iranian urologists are highly skilled and internationally trained, offering a wide range of specialized treatments and surgeries for urological conditions, including kidney stones, prostate cancer, and urinary tract disorders. Moreover, Iran boasts state-of-the-art medical facilities, equipped with modern technology, and offers cost-effective medical services compared to many Western countries, making it an attractive destination for patients seeking high-quality urological care while minimizing financial burdens.
Urology in Iran is a medical specialty focused on diagnosing and treating disorders of the urinary tract and male reproductive system. Urologists are trained to address a broad spectrum of conditions, including kidney stones, urinary tract infections, prostate problems, infertility, and urological cancers such as prostate, bladder, and kidney cancer. They utilize various diagnostic tools and surgical techniques, ranging from minimally invasive procedures to complex surgeries, to provide effective care and improve patients’ quality of life related to urological health concerns.

Ipdtourism is a highly reputable choice for international travelers due to its commitment to providing exceptional services. With a wealth of experience in the tourism industry, Ipdtourism specializes in creating memorable and seamless travel experiences for visitors from around the world. Their team of dedicated professionals is well-versed in catering to the diverse needs and preferences of travelers, offering a wide range of customizable packages that encompass cultural, historical, and adventure-based tours.
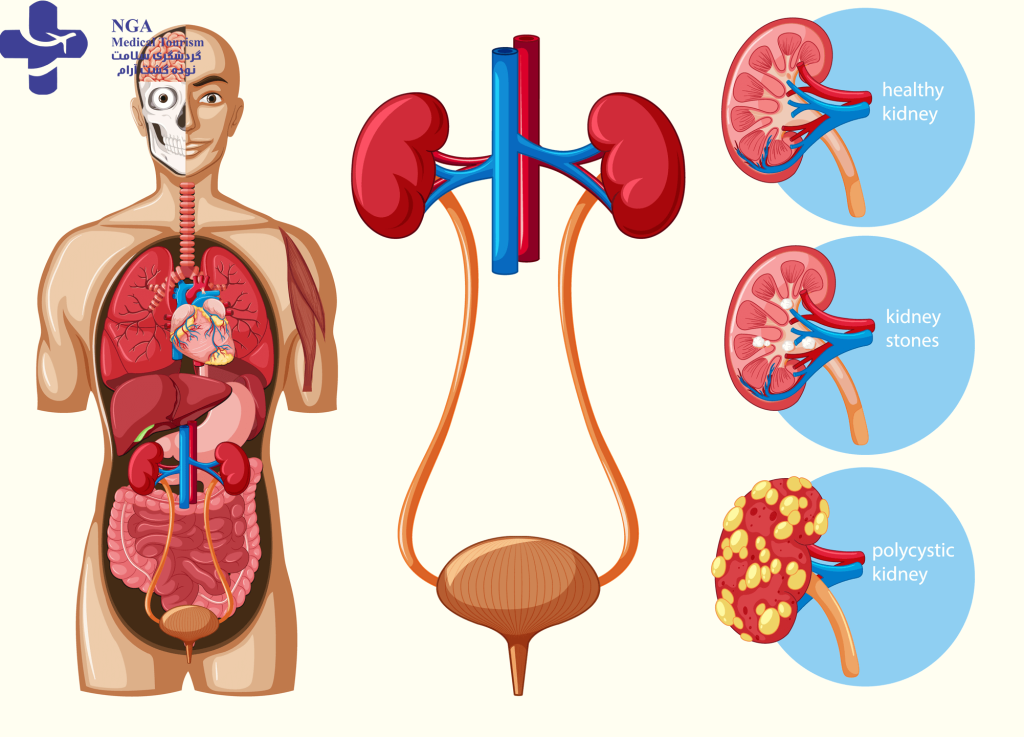
Urology in Iran is a specialized branch of medical science dedicated to the surgical and medical treatment of the urinary tract and male reproductive organs, while in females, it typically excludes interventions related to the genital tract and reproduction. Urologists examine and address conditions involving the kidneys, adrenal glands, bladder, prostate, urinary tract, testicles, epididymis, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, and penis. Common urological issues encompass urinary tract infections, kidney stones, bladder control disorders, and prostate disorders, among others. Urologists conduct comprehensive assessments, including physical examinations of the genitourinary system, as well as evaluations of other relevant bodily systems, sometimes involving genital and digital rectal examinations to assess prostate health.
Urology in Iran and nephrology are both medical specialties that deal with disorders of the urinary tract and kidneys, but there are some important differences between the two. Here are some key differences:
1. Focus of treatment: Urologists focus on the surgical and medical management of conditions affecting the urinary tract and male reproductive system. Nephrologists, on the other hand, specialize in the diagnosis and management of kidney disorders, including kidney disease, kidney failure, and hypertension related to kidney problems.
2. Areas of expertise: Urologists have specialized training in surgical techniques, including minimally invasive procedures, to treat conditions such as kidney stones, urinary tract infections, and prostate cancer. Nephrologists have expertise in managing conditions related to kidney function, including electrolyte imbalances, hypertension, and chronic kidney disease.
3. Diagnostic tools: Urologists use diagnostic tools such as urine tests, imaging studies, and cystoscopy to diagnose and evaluate conditions affecting the urinary tract and male reproductive system. Nephrologists use a range of diagnostic tools, including blood tests, urine tests, and imaging studies, to evaluate the function of the kidneys and diagnose kidney disorders.
4. Treatment options: Urologists use a range of treatment options, including medications, minimally invasive procedures, and surgery, to manage conditions affecting the urinary tract and male reproductive system. Nephrologists use medications, lifestyle modifications, and dialysis to manage kidney disorders and kidney failure.
While there is some overlap between urology and nephrology, these are distinct specialties with different areas of focus and expertise. Patients with urological or kidney-related concerns should consult with the appropriate specialist based on their specific symptoms and medical history.
Enlarged prostate disease, or benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), is a prevalent ailment among aging men, causing urinary issues like increased frequency and weakened urine flow.
An overactive or frequency bladder is a condition characterized by improper bladder muscle contractions, leading to frequent and urgent urination.
Prostate cancer is a potentially life-threatening disease primarily affecting men. Early detection through screening is crucial for successful treatment.
Microscopic hematuria refers to the presence of blood in the urine that is only detectable under a microscope. This condition can be an indicator of underlying health issues, and seeking medical evaluation is essential.
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is a common bacterial infection that can affect any part of the urinary system, including the bladder, kidneys, ureters, and urethra. UTIs often cause symptoms such as pain during urination, frequent urination, and discomfort in the lower abdomen.
Impotence, also known as erectile dysfunction (ED), is a condition where a man has difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection sufficient for sexual intercourse.
Impotence, also known as erectile dysfunction (ED), is a condition where a man has difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection sufficient for sexual intercourse.
Bladder cancer is a malignancy that forms in the tissues of the bladder, often causing symptoms like blood in the urine and increased urinary frequency.
Urology Tests, Procedures, and Surgeries
Urologists use a variety of tests, procedures, and surgeries to diagnose and treat urologic conditions. Here are some examples:
1. Urinalysis: A test to analyze the urine for signs of infection, blood, or abnormal cells.
2. Cystoscopy: A procedure that allows the urologist to view the inside of the bladder and urethra using a thin, flexible tube with a camera.
3. Ultrasound: A non-invasive imaging test that uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the urinary tract and male reproductive system.
4. Biopsy: A procedure to remove a small sample of tissue for examination under a microscope to diagnose cancer or other conditions.
5. Urodynamic testing: A series of tests to evaluate the function of the urinary tract, including the bladder and urethra.
6. Lithotripsy: A non-invasive procedure that uses shock waves to break up kidney stones into smaller pieces that can be passed more easily.
7. Prostatectomy: A surgical procedure to remove the prostate gland, commonly used to treat prostate cancer.
8. Nephrectomy: A surgical procedure to remove a kidney, typically used to treat kidney cancer or severe kidney disease.
9. Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP): A surgical procedure to remove part of the prostate gland to relieve urinary symptoms caused by an enlarged prostate.
10. Radical cystectomy: A surgical procedure to remove the bladder and surrounding lymph nodes, typically used to treat bladder cancer.
11. Testicular prosthesis: A surgical procedure to implant an artificial testicle to replace a missing or removed testicle.
These are just a few examples of tests, procedures, and surgeries that urologists use to diagnose and treat urologic conditions. The specific tests or procedures recommended will depend on the individual patient’s symptoms and medical history.
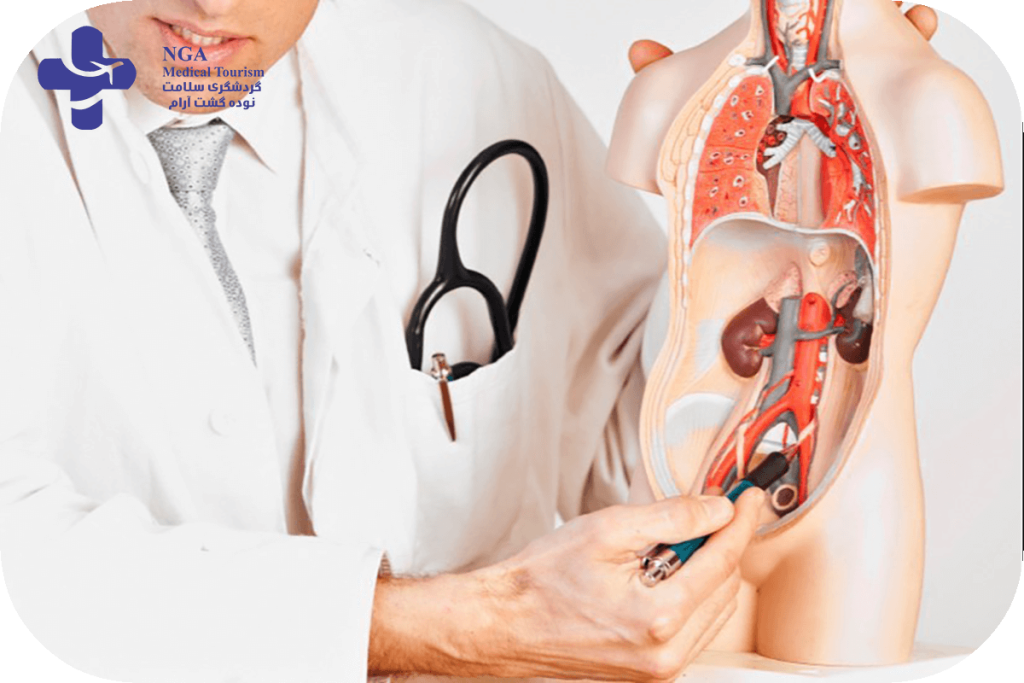
The Urology-Body Connection
Urology in Iran is a medical specialty that focuses on the diagnosis and treatment of conditions related to the urinary tract and male reproductive system. However, there are many ways in which urological conditions can impact the body as a whole. Here are some examples of the urology-body connection:
- Kidney function
- Sexual function
- Incontinence
- Cancer risk
- Overall health
Overall, the urology-body connection highlights the importance of treating urological conditions promptly and effectively to protect not only the urinary system but also the overall health and well-being of the body. Urologists work closely with other healthcare professionals, such as nephrologists and oncologists, to provide comprehensive care to patients with urological conditions.
- The Bladder
- Kidneys
- Adrenal glands (located on top of each kidney)
- Ureters
- Urethra
- Testes
- Epididymis
- Vas deferens
- Seminal vesicles
- Prostate gland
- Penis
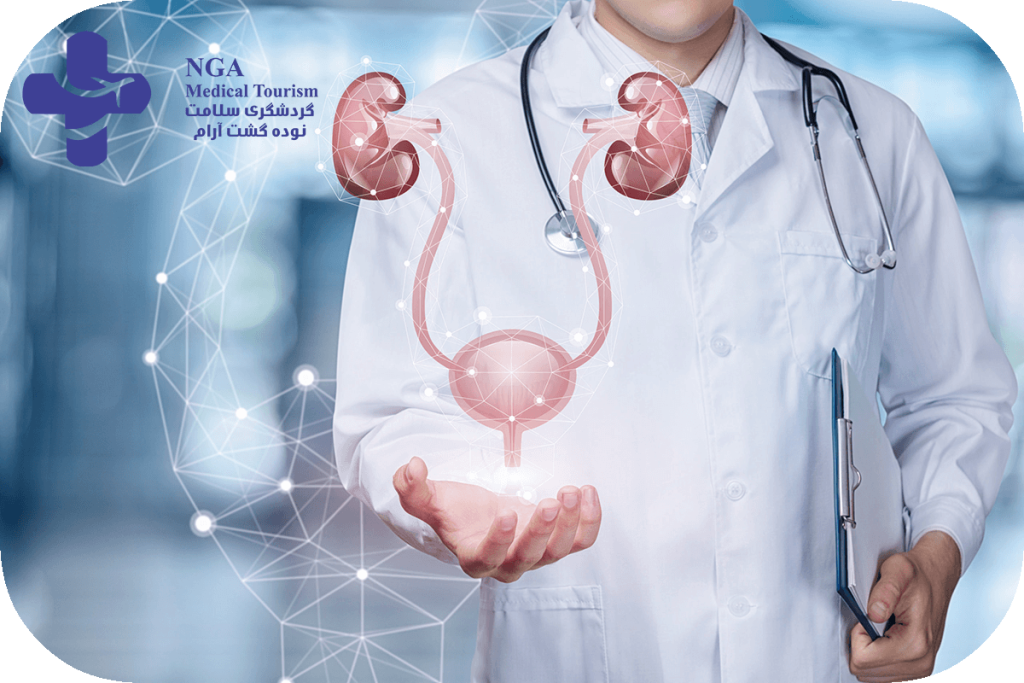
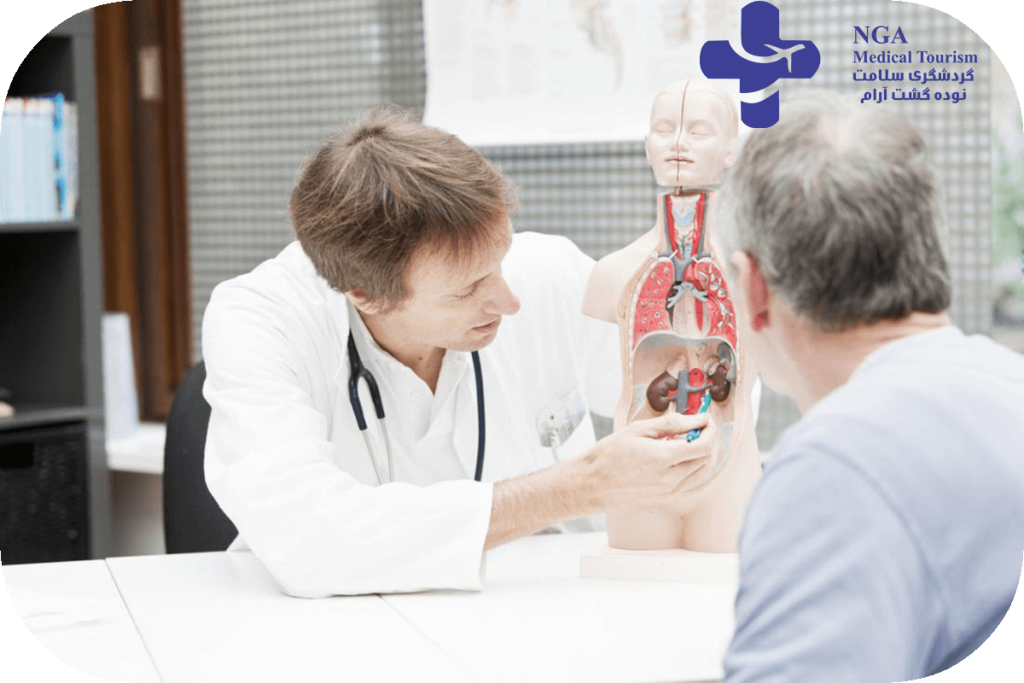
Who is a urologist?
Urologists are skilled in both medical and surgical approaches to managing urologic problems. They use a variety of diagnostic tools, such as urine tests, blood tests, imaging studies, and cystoscopy, to evaluate urologic conditions and develop a treatment plan tailored to the individual patient’s needs.
In addition to diagnosing and treating urologic conditions, urologists also play an important role in preventative care. They may advise patients on lifestyle modifications or prescribe medications to reduce the risk of urologic conditions or prevent their recurrence.
- The Bladder
- Kidneys
- Adrenal glands (located on top of each kidney)
- Ureters
- Urethra
- Testes
- Epididymis
- Vas deferens
- Seminal vesicles
- Prostate gland
- Penis
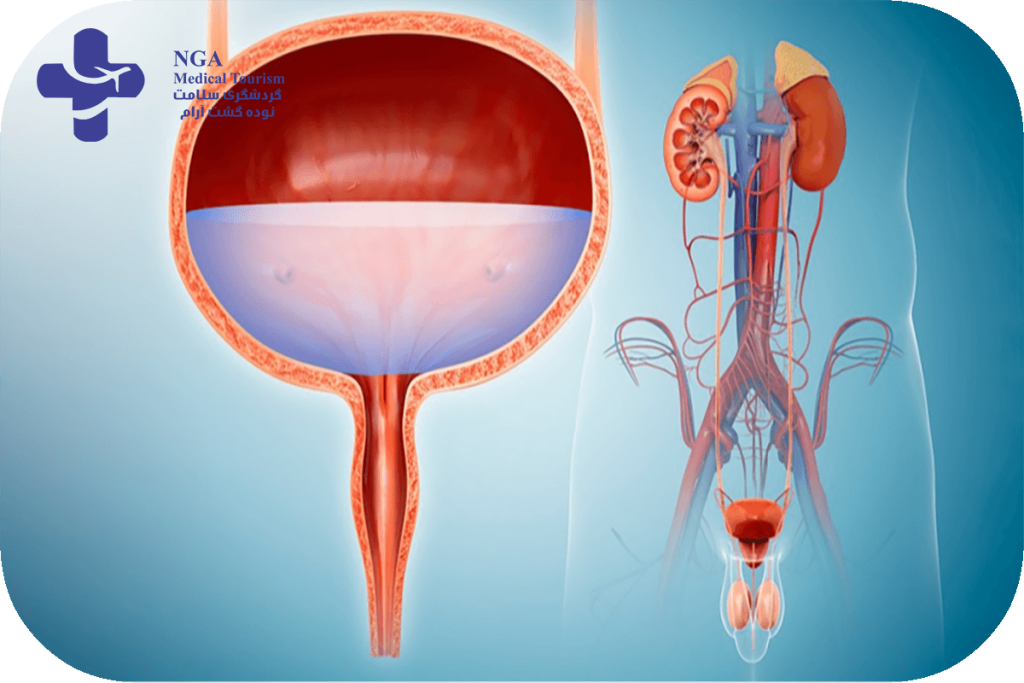
the best urologist in iran
for Finding the best urology in Iran, specializing in urology in Iran, Stay tuned for a list of some of the top Iranian urologists in the following paragraphs.
Dr. Nasser Simforosh – Specialist in kidney and urinary tract surgery
Dr. Mohammad Reza Norouzi – Surgeon and specialist in kidney and urinary tract
Dr. Mohsen Ziaei – Urological Surgeon
Dr. Abbas Basiri – Kidney, Urinary and Genital Surgeon
Dr. Seyed Amin Mirsadeghi – Surgeon and specialist in kidney and urinary tract
Dr. eslami – Surgeon and specialist in kidney and urinary tract
Urologists offer a wide range of treatments for conditions related to the urinary tract and male reproductive system. The specific treatment options recommended will depend on the individual patient’s symptoms and medical history. Here are some examples of treatments that a urologist may offer:
1. Medications: Urologists may prescribe medications to treat conditions such as urinary tract infections, erectile dysfunction, overactive bladder, or prostate problems.
2. Minimally invasive procedures: Urologists may use minimally invasive procedures to treat conditions such as kidney stones or an enlarged prostate. These procedures typically involve using a small camera and instruments to access and treat the affected area.
3. Surgery: Urologists are trained in a variety of surgical techniques to treat conditions such as bladder cancer, prostate cancer, or kidney cancer. They may also perform surgical procedures to treat conditions such as incontinence or pelvic organ prolapse.
4. Radiation therapy: Urologists may work with radiation oncologists to provide radiation therapy to treat certain urologic conditions, such as prostate cancer.
5. Dialysis: If a patient’s kidneys are not functioning properly, urologists may work with nephrologists to provide dialysis, which is a procedure that helps filter waste and excess fluids from the blood.
6. Lifestyle modifications: Urologists may recommend lifestyle modifications, such as changes to diet or exercise habits, to help manage certain urologic conditions, such as kidney stones or urinary incontinence.

What Diseases Do Urologists Treat?
In men, urologists commonly treat:
- Cancers of the bladder, kidneys, penis, testicles, adrenal and prostate glands
- Prostate gland enlargement known as benign prostatic hyperplasia
- Erectile dysfunction
- Male infertility
- Interstitial cystitis and other bladder disorders
- Kidney diseases and kidney stones
- Prostatitis, which is inflammation of the prostate gland
- Urinary tract infections
- Varicoceles, or enlarged veins in the scrotum
- Urethral stricture
In women, urologists often treat:
- Urinary incontinence
- Bladder prolapse, or the dropping of the bladder into the vagina
- Cancers of the bladder, kidneys, and adrenal glands
- Bladder conditions, such as interstitial cystitis and overactive bladder
- Kidney and ureteral stones
- Urinary tract infections
Read More: IVF in Iran
Read More: What Is Ivf Procedure
Read More: Where Is The Cheapest Country For IVF In 2023?
Read More: Ivf Injections
What Surgeries Do Urologists Perform?
Urologists perform a wide range of surgical procedures to diagnose and treat conditions related to the urinary tract and male reproductive system. Here are some examples of surgeries that urologists commonly perform:
1. Prostatectomy: A surgical procedure to remove the prostate gland, typically used to treat prostate cancer.
2. Nephrectomy: A surgical procedure to remove a kidney, typically used to treat kidney cancer or severe kidney disease.
3. Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP): A surgical procedure to remove part of the prostate gland to relieve urinary symptoms caused by an enlarged prostate.
4. Radical cystectomy: A surgical procedure to remove the bladder and surrounding lymph nodes, typically used to treat bladder cancer.
5. Orchiectomy: A surgical procedure to remove one or both testicles, typically used to treat testicular cancer.
6. Ureteroscopy: A minimally invasive surgical procedure to treat kidney stones or other obstructions in the ureter or kidney.
7. Penile prosthesis surgery: A surgical procedure to implant a device that helps achieve an erection, typically used to treat severe cases of erectile dysfunction.
8. Vesicoureteral reflux surgery: A surgical procedure to correct a condition in which urine flows backwards from the bladder into the ureters, typically used in children with recurring urinary tract infections.
These are just a few examples of the many surgical procedures that urologists perform. The specific surgery recommended will depend on the individual patient’s symptoms, medical history, and the condition being treated. Urologists may also use minimally invasive techniques, such as laparoscopy or robot-assisted surgery, to perform some of these procedures, which can result in less pain, scarring, and recovery time compared to traditional open surgery.


What are the subspecialty areas of urology?
Urologists are skilled in both medical and surgical approaches to managing urologic problems. They use a variety of diagnostic tools, such as urine tests, blood tests, imaging studies, and cystoscopy, to evaluate urologic conditions and develop a treatment plan tailored to the individual patient’s needs.
In addition to diagnosing and treating urologic conditions, urologists also play an important role in preventative care. They may advise patients on lifestyle modifications or prescribe medications to reduce the risk of urologic conditions or prevent their recurrence.
What lifestyle adjustments can people make to improve their urologic health?
- Stay hydrated
- Practice good hygiene
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Quit smoking
- Manage chronic conditions
- Practice safe sex
- Avoid holding urine
The cost of urology services in Iran can vary depending on the type of service required, the location of the medical facility, and the experience of the medical professional. However, in general, medical services in Iran are known to be relatively affordable compared to other countries.
For example, the cost of a routine urology consultation in Iran can range from 500,000 to 1,500,000 Iranian Rials (IRR), which is approximately 20-60 USD, depending on the location and the medical facility.
The cost of urologic in Iran, such as prostate surgery or kidney stone removal, can vary widely depending on the complexity of the procedure, the type of anesthesia used, and the length of hospital stay. However, in general, the cost of urologic surgeries in Iran is significantly less expensive compared to other countries.
It’s important to note that these are rough estimates and the actual cost can vary widely based on individual circumstances.
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
Urinary tract infections are the most common type of urologic problem and occur much more frequently in women. In fact, close to 60 percent of women will experience a UTI at some point in their life, while UTIs affect only 12 percent of men.
List of urological topics
Benign prostatic hyperplasia.
Bladder cancer.
Bladder stones.
Cystitis.
Development of the urinary and reproductive organs.
Epididymitis.
Erectile dysfunction.
Interstitial cystitis.
A urologist is a specialist surgeon who treats anyone with a problem with their kidneys, bladder, prostate and male reproductive organs. These include a wide range of conditions, for example, cancer, kidney stones, infection, incontinence, sexual dysfunction and pelvic floor problems.
Acute Urinary Retention. The sudden inability to urinate can cause extreme pain and demands immediate treatment. …
Testicular Torsion. …
Priapism. …
Paraphimosis. …
Fournier’s Gangrene.
Urofacial syndrome (UFS) is an extremely rare inherited disorder characterized by an unusual facial expression and disorder of the urinary tract (uropathy). When the bladder tries to empty, the outlet closes, meaning that the urine goes back towards the kidneys rather than out of the body.
- CYSTOSCOPY.
- ENDOSCOPES.
- FORCEPS / FOREIGN BODY (FOR BLADDER)
- FORCEPS / KIDNEY / KIDNEY STONE.
- FORCEPS / OPTICAL STONE FORCEPS.
- FORCEPS / URETHRO.
- INSTRUMENTS / BASIC / ADULT.
Women, for example, may be more comfortable seeing a gynecologist, nurse midwife, or other women’s health practitioner for STD testing and treatment. Men who are wondering where to get treated for STDs might choose to go to a urologist.
- Vasectomy. This is a common urology procedure that many men get. …
- Vasectomy Reversal. …
- Cystoscopy. …
- Prostate Procedures. …
- Ureteroscopy. …
- Lithotripsy. …
- Orchiopexy. …
- Penile Plication.
Kidney stones are hard mineral and salt deposits that form in the kidneys and can cause severe pain and urinary complications.
refers to a sudden and rapid loss of kidney function, often caused by factors such as dehydration, medication toxicity …
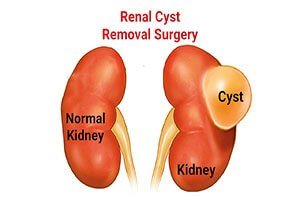
Kidney cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form in the kidneys and can vary in size, potentially leading to complications or…
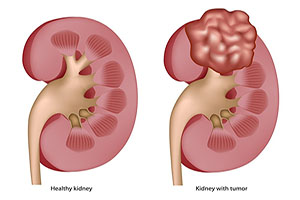
refers to the abnormal and uncontrolled growth of cells in the kidneys, which can lead to the formation of tumors …
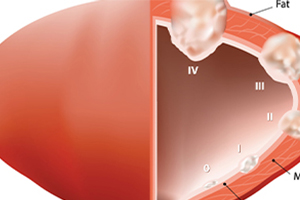
Bladder cancer is a cancer that develops in the lining of the bladder and can cause symptoms such as blood in the urine …
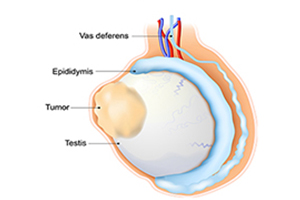
Testicular cancer is a cancer that develops in the testicles and can cause symptoms such as a lump or swelling in the testicle, pain …
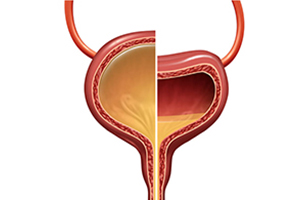
Overactive bladder is a condition in which the bladder muscle contracts involuntarily, causing symptoms such …
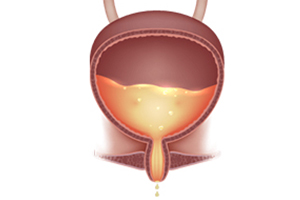
Incontinence refers to the loss of bladder or bowel control and can be caused by a variety of factors, including weak pelvic…


