- 10 July, 2023
- blog
open heart surgery:
Open heart surgery, also known as cardiac surgery or cardiothoracic surgery, is a medical procedure in which the chest is opened to access the heart. During open heart surgery, the patient’s heart is temporarily stopped, and a heart-lung machine takes over the function of pumping blood and oxygen to the body. This allows the surgeon to perform various cardiac procedures, such as repairing or replacing heart valves, correcting congenital heart defects, performing coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) to treat blocked arteries, or addressing other complex heart conditions. Open heart surgery is a major surgical intervention and is typically reserved for cases where less invasive treatments are not feasible or effective. Patients undergo careful evaluation before the procedure, and recovery may involve a hospital stay of several days to weeks, depending on the specific surgery and individual factors.
open heart surgery recovery:
Hospital Stay
Patients typically spend several days in the hospital after open heart surgery, with the exact duration varying based on the type of surgery and individual health factors.
Pain Management
Pain at the surgical site is common and managed with medications prescribed by the healthcare team.
Mobility
Early mobility and breathing exercises are encouraged to prevent complications like pneumonia and blood clots.
Diet
Patients start with a liquid diet and gradually progress to solid foods as tolerated. Nutrition plays a vital role in the healing process.
Medications
Patients are often prescribed medications to manage pain, prevent infection, and control blood pressure and other cardiovascular factors.
Wound Care
Patients are taught how to care for their surgical incisions, which should be kept clean and dry.
Cardiac Rehabilitation
Many patients benefit from cardiac rehabilitation programs, which include supervised exercise, education, and support to improve cardiovascular health.
Follow-Up Appointments
Regular follow-up appointments with the surgical team and cardiologist are essential to monitor progress and adjust treatment plans as needed.
Resuming Activities
The timeline for resuming normal activities varies, but most patients can gradually return to light activities within a few weeks and resume more strenuous activities over several months.
Emotional Support
Recovery can be emotionally challenging, and patients may benefit from counseling or support groups to address anxiety, depression, or other emotional aspects of the healing process.
open heart surgery survival rate
The survival rate for open heart surgery varies based on factors such as the type of procedure, patient health, and surgical expertise, but generally, open heart surgery is associated with high success rates. Procedures like coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) and heart valve surgery often have favorable outcomes, with the majority of patients surviving and experiencing improved cardiac health. Advances in surgical techniques and post-operative care have contributed to enhanced survival rates over time.
long-term side effects of open heart surgery
Long-term side effects of open heart surgery can include the risk of developing complications such as infection, scarring, or blood clot formation at the surgical site, as well as potential issues related to the use of heart-lung bypass machines, such as kidney problems or cognitive changes. Some patients may experience long-term pain or discomfort at the incision site or in the chest area. Additionally, open heart surgery may require ongoing medication regimens, lifestyle adjustments, and regular cardiac check-ups to manage cardiovascular risk factors and monitor the health of the heart. It’s essential to note that the specific long-term side effects can vary depending on the type of surgery, the patient’s individual health, and the presence of any underlying medical conditions. Patients should maintain open communication with their healthcare team to address any concerns and receive appropriate follow-up care to optimize their long-term health and well-being.
Bypass surgery, also known as coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), is a common cardiac procedure used to treat coronary artery disease. During bypass surgery, a cardiothoracic surgeon grafts healthy blood vessels, often taken from the patient’s own body, to reroute blood flow around blocked or narrowed coronary arteries, restoring proper blood supply to the heart muscle. This procedure alleviates chest pain (angina), reduces the risk of heart attack, and improves overall heart function.
Is bypass surgery, open heart?
Bypass surgery, also known as coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), is a common cardiac procedure used to treat coronary artery disease. During bypass surgery, a cardiothoracic surgeon grafts healthy blood vessels, often taken from the patient’s own body, to reroute blood flow around blocked or narrowed coronary arteries, restoring proper blood supply to the heart muscle. This procedure alleviates chest pain (angina), reduces the risk of heart attack, and improves overall heart function.
Difference between bypass and open heart surgery
Open-heart surgery and bypass surgery both entail chest incisions, but they differ in scope and purpose. Open-heart surgery refers to any procedure that necessitates opening the chest, irrespective of whether the heart itself is accessed; it may encompass operations on various chest components like heart arteries, valves, or muscles. Bypass surgery, on the other hand, is a specific form of open-heart surgery among various cardiac procedures, including angioplasty and heart transplants. Notably, bypass surgery may or may not involve opening the heart, and it entails grafting a blood vessel, often from the chest or leg, onto a blocked coronary artery, creating an alternate route for blood flow. The execution of bypass surgery can be either through open-heart surgery or less invasive methods, depending on the case.
When Do You Need Heart Surgery?
Heart surgery may be necessary in the following conditions:
- Blockage in the left main coronary artery.
- Severe chest pain caused by blockages in multiple arteries responsible for blood supply to the body.
- Narrowing of an artery after a previous procedure.
- A condition within the coronary arteries affecting the left ventricle’s function.
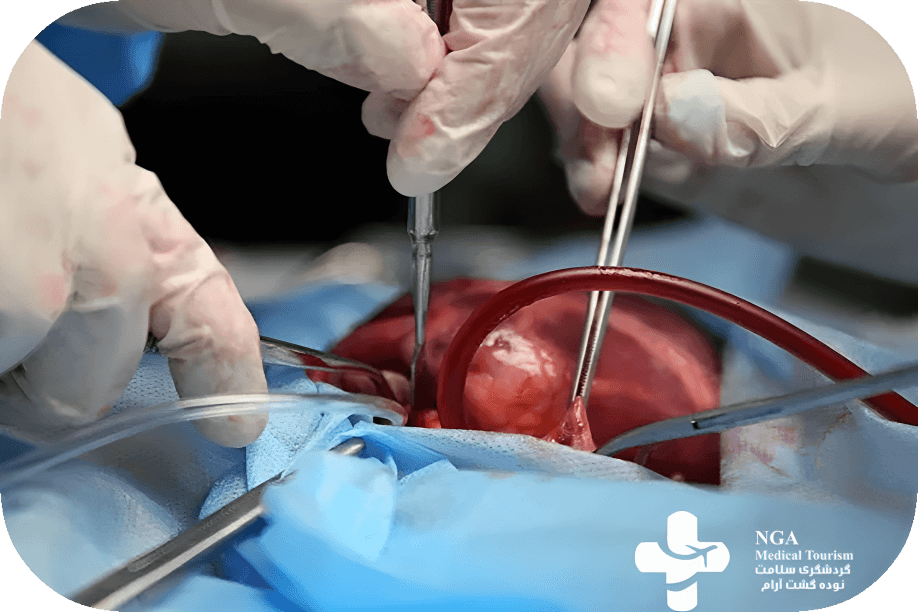
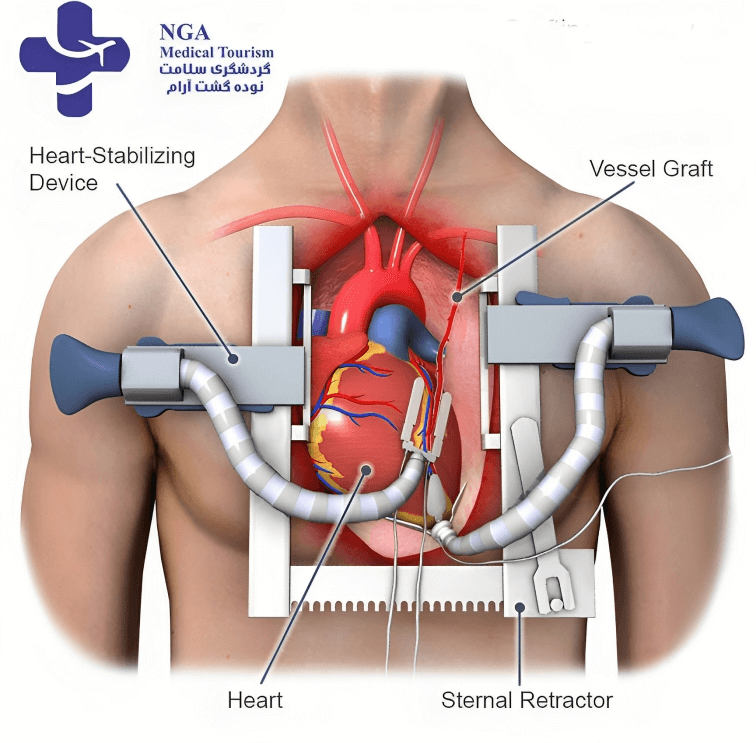
Procedure of Open Heart Surgery
In a coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) procedure, the patient undergoes general anesthesia as the surgeon makes an incision in the chest, often dividing the breastbone. Using a healthy blood vessel from the chest or leg, the surgeon creates a new path for blood to bypass a blocked coronary artery. A heart-lung bypass machine may be used. After grafting, the breastbone is secured, and the incision is closed with stitches. Procedure details can vary based on the patient’s condition and the chosen surgical approach.
When is Bypass Surgery Needed?
Bypass surgery is typically recommended when:
- Medical Treatment Isn’t Effective
- Multiple Blocked Coronary Arteries
- Left Main Coronary Artery Disease
- Complex Coronary Artery Disease
- Heart Attack Recovery
The decision to undergo bypass surgery is typically made by a cardiologist or a cardiac surgeon after a thorough evaluation of the patient’s condition, taking into account factors like the location and severity of blockages, overall health, and the presence of symptoms.
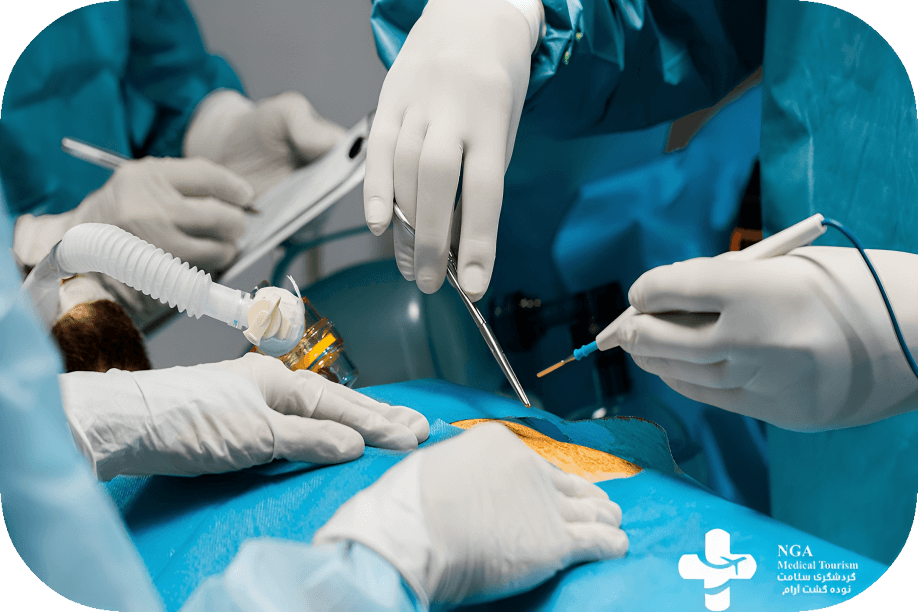
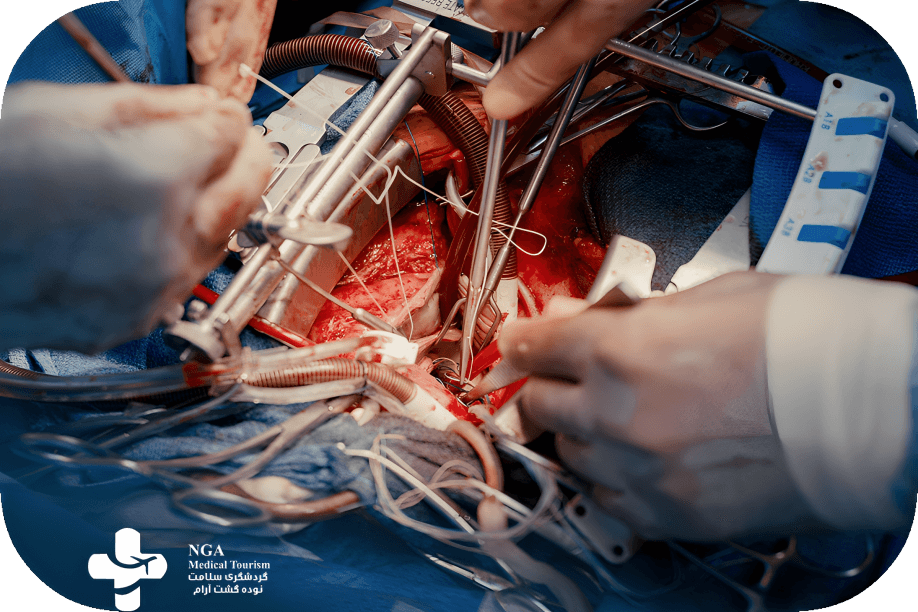
Procedure of Bypass Surgery
In a coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) procedure, the patient undergoes general anesthesia as the surgeon makes an incision in the chest, often dividing the breastbone. Using a healthy blood vessel from the chest or leg, the surgeon creates a new path for blood to bypass a blocked coronary artery. A heart-lung bypass machine may be used. After grafting, the breastbone is secured, and the incision is closed with stitches. Procedure details can vary based on the patient’s condition and the chosen surgical approach.
How To Take Care Of A Patient After Bypass Surgery?
The initial recovery phase typically spans 6-8 weeks, and hospital discharge requires the surgeon’s assurance of normal progress. Strict adherence to the doctor’s provided instructions is vital for a healthy recovery without complications. To facilitate a speedy recuperation, keep the wound consistently clean to prevent infection, promptly notify the doctor of any fever exceeding 100°F, redness, burning sensations, or excessive blood drainage. Specific guidelines for daily activities will be provided by the doctor, including avoiding heavy lifting, limiting prolonged standing, daily walking, and stair climbing unless advised otherwise. Resuming driving should be approved by the doctor, and it’s advisable to maintain a healthy diet while avoiding spicy or fried foods.
Iran has emerged as a prominent destination for medical tourism, attracting patients from around the world seeking high-quality healthcare at affordable prices. With its advanced medical facilities, skilled healthcare professionals, and cost-effective treatments, Iran offers a compelling option for individuals seeking medical treatments abroad.
Here are some key factors that make Iran an attractive destination for medical tourists:
Quality Healthcare: Iran boasts world-class medical infrastructure and facilities equipped with state-of-the-art technology. The country is home to highly qualified and experienced doctors, surgeons, and healthcare professionals who provide exceptional medical care across various specialties.
Cost-Effective Treatments: One of the primary advantages of seeking medical treatment in Iran is the significantly lower costs compared to other countries. Medical procedures, surgeries, and treatments in Iran are often more affordable without compromising on quality. Cost of Bypass And Open Heart Surgery in Iran, makes Iran an appealing choice for patients seeking value-for-money healthcare solutions.
Conclusion:
It is indeed crucial to consider the financial aspect when it comes to major surgeries like open heart surgery and bypass surgery. These procedures can involve significant costs, including hospital expenses, surgeon fees, medications, and post-operative care.
IPD Tourism, as one of the leading healthcare tourism companies, offers you the opportunity to benefit from state-of-the-art medical services and highly qualified healthcare professionals comparable to top-quality treatment standards worldwide. Moreover, in addition to receiving excellent medical care, you can also have a memorable journey in this historical and beautiful land at a significantly lower cost.
Read More: Arteriovenous Malformations
Read More: Aortic Valve Stenosis (Aortic Stenosis)
Read More: Heart Valve Surgery
Read More: Cardiology in Iran
Read More: General Heart Surgery
FAQ
Open heart surgery involves making incisions in the patient’s chest to access the heart, while bypass surgery is a specific type of open-heart surgery. Bypass surgery can be performed either off-pump (beating heart surgery) or on-pump, depending on the technique used during the remainder of the procedure.
Bypass surgery carries certain short-term risks, including the possibility of heart attack, stroke, kidney problems, and even death. The level of risk can vary depending on the individual’s overall medical condition and health. Additionally, there are other potential risks associated with surgery, such as complications related to anesthesia administration and the risk of infection at the site of the chest incision.
The patient will be placed on a ventilator for the procedure, but a cardiopulmonary bypass machine is not required. Coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery is the only open-heart procedure that is performed off-pump.
Coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery typically has a duration of 3 to 6 hours, although the actual time may vary depending on the number of blood vessels being connected. The surgeon may use blood vessels sourced from different areas of the body, such as the leg (saphenous vein), the chest (internal mammary artery), or the arm (radial artery), to perform the grafting procedure.
Sometimes, despite a previous heart surgery, problems can worsen or complications can arise with the tissues used for replacement. In such situations, additional heart surgery (or surgeries) may be necessary to maintain overall heart health. These subsequent surgeries are performed to address ongoing issues and ensure the well-being of the patient’s heart.
Patients with severe diffuse coronary disease have the option to undergo multiple bypass grafting procedures, even up to eight or more surgeries. These procedures have shown low mortality rates and improved exercise tolerance and functional classification in such patients.
As many as four major blocked coronary arteries can be bypassed during one surgery.
There is insufficient evidence to confirm whether on-pump open heart surgery is safer than off-pump surgery. However, according to the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE), survival rates 1 year after either form of open-heart surgery are similar at about 96–97 percent.