All Departments
- Aortic valve stenosis (Aortic stenosis)
- arteriovenous malformations
- Avascular Necrosis
- Best cosmetic dentistry in Iran| Dental Treatment in Iran
- Breast Augmentation in Iran|Breast implant in iran
- Breast Reduction surgery
- Cancer in Iran: oncology in Iran
- Cardiology
- Cataract surgery in Iran
- Cochlear Implant Surgery in Iran
- Cosmetic Laser
- Cosmetic Surgery
- Ear cosmetic surgery
- Eye Care
- Eyelid surgery (Blepharoplasty)
- General Heart Surgery in Iran
- General surgery in Iran
- Glaucoma Treatment In Iran
- Hair Transplant
- Heart valve surgery
- lasik Eye Surgery
- Liposuction
- Non-Surgical Cosmetic procedures in iran
- Organ Transplantation in Iran
- Orthopedic
- Paget disease of bone
- Pediatrics
- Plastic surgery
- Psychiatry
- Radiology
- Rhinoplasty surgery in iran
- Shoulder Replacement Surgery
- SkinCare Treatment
- Spinal cord injury
- urolithiasis procedure in iran
- Urology
- Varicocelectomy
Opening Hours

Paget disease of bone
Iran is a suitable choice for Paget’s disease treatment due to its skilled medical professionals, cost-effective healthcare services compared to neighboring and European countries, and its growing popularity as a medical tourism destination. With an abundance of experienced specialists, modern medical facilities, and competitive prices, we offers a compelling option for individuals seeking effective and affordable treatment for Paget’s disease in Iran.
Paget’s disease of the bone, also known as osteitis deformans, is a chronic and often asymptomatic bone disorder characterized by abnormal bone remodeling. In this condition, bones become enlarged, weaker, and prone to fractures. It can affect one or more bones and is typically diagnosed through imaging and blood tests that reveal elevated markers of bone turnover.


Ipdtourism is your reliable partner for all your Paget’s bone disease treatment needs in Iran. Our dedicated team specializes in offering comprehensive and seamless solutions for international patients seeking top-quality Paget’s disease procedures. From the moment you decide to begin your Paget’s bone disease treatment journey to the successful completion of the procedure, Ipdtourism handles every aspect, ensuring you receive the best care and support in Iran.
paget's disease
Paget’s disease in Iran, or Paget’s disease of bone, is a chronic and typically asymptomatic skeletal disorder characterized by abnormal bone remodeling. In this condition, bones in the body undergo a cycle of excessive breakdown and formation, leading to enlarged, weakened, and deformed bones. Although the exact cause remains unclear, genetic and environmental factors are thought to contribute. Paget’s disease is often diagnosed incidentally through imaging or blood tests that show elevated markers of bone turnover.
Paget’s disease of bone, also known as osteitis deformans, is a chronic skeletal disorder characterized by abnormal bone remodeling. This condition leads to the enlargement and weakening of affected bones, making them more prone to fractures and deformities. While the exact cause remains uncertain, a combination of genetic and environmental factors is believed to contribute. Diagnosis is typically based on imaging studies and blood tests, revealing elevated markers of bone turnover. Treatment options include medications like bisphosphonates to slow down the excessive bone remodeling process and, in severe cases, surgical intervention. Regular monitoring is crucial to assess disease progression and prevent complications, with the goal of preserving bone health and function in individuals with Paget’s disease of bone.
paget's disease of breast
Paget’s disease of the breast, also known as mammary Paget’s disease, is a rare type of breast cancer that typically originates in the ducts of the breast and affects the nipple and areola. It is characterized by symptoms such as itching, redness, scaling, and sometimes nipple discharge or inversion. Paget’s disease of the breast is often associated with an underlying ductal carcinoma, and diagnosis typically involves a combination of clinical examination, mammography, and biopsy. Treatment options may include surgery to remove the affected tissue, often combined with radiation therapy and, in some cases, chemotherapy or hormone therapy. Early detection and comprehensive treatment are crucial for improving the prognosis of individuals with Paget’s disease of the breast.
Read More: Orthopedic in Iran
Read More: Shoulder Replacement Surgery
Read More: Spinal cord injury treatment in Iran
Read More: Avascular Necrosis treatment in Iran
Read More: Paget Disease Of Bone treatment in iran
paget's disease of bone symptoms:
Bone Pain
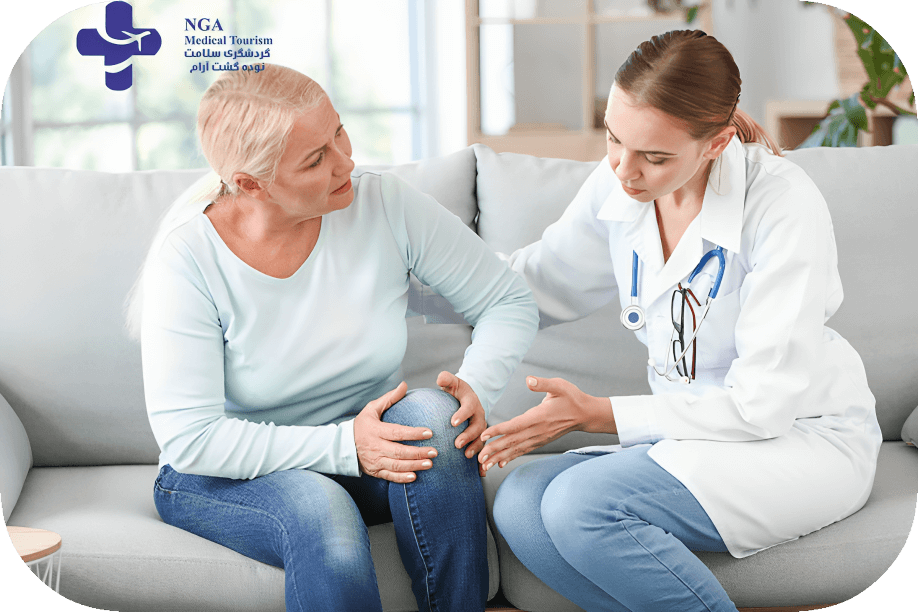
The most common symptom is bone pain, which may be dull, aching, or throbbing. It often occurs in the bones affected by the disease, such as the pelvis, spine, legs, or skull.
Bone Deformities
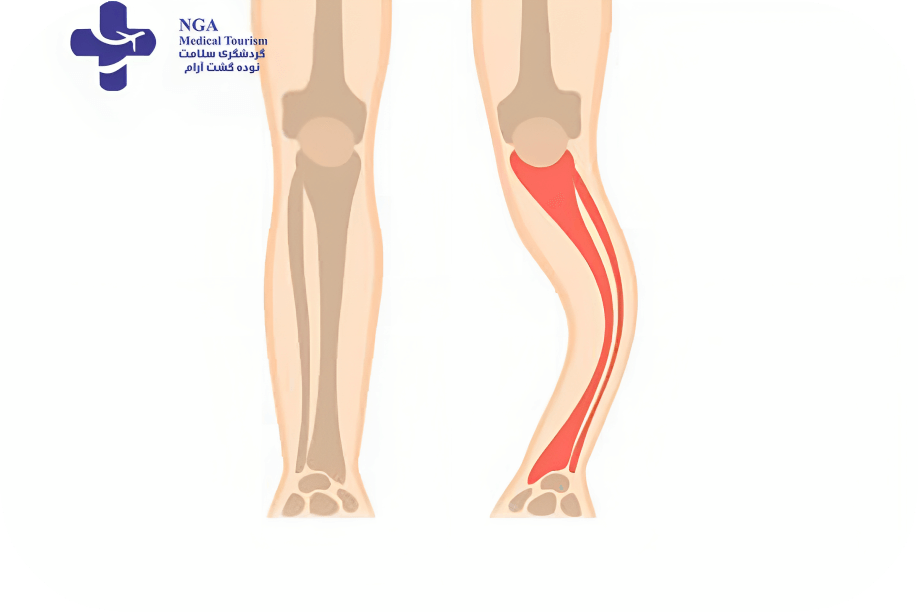
As Paget’s disease progresses, it can lead to bone deformities, such as bowing of the legs or an enlarged skull.
Fractures
Weakened and deformed bones are more prone to fractures, which can occur even with minor trauma or stress on the bone.
Joint Pain
If the disease affects the joints, it can cause joint pain and stiffness.
Hearing Loss
If the bones in the skull are affected, it can lead to hearing loss or other neurological symptoms.
Headaches
Enlargement of the skull bones can result in headaches.
Nerve Compression
In rare cases, Paget’s disease may compress nearby nerves, leading to symptoms such as numbness or tingling.
Causes of Paget’s Disease
Paget’s disease of bone, also known as Paget’s disease, is a condition whose exact cause remains unknown to medical experts. However, there is a growing understanding that a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental factors may contribute to its development. Researchers have identified specific gene alterations that could increase an individual’s susceptibility to Paget’s disease. Additionally, ongoing investigations are exploring the potential role of certain viruses in triggering the disease, particularly in individuals with pre-existing risk factors. Notably, some research indicates that in certain countries, both the prevalence and severity of Paget’s disease may be on the decline, suggesting possible shifts in disease patterns over time.
paget's disease of bone symptoms
Paget’s disease in Iran, can manifest with symptoms such as bone pain, which is often dull and aching, bone deformities like bowing of the legs or an enlarged skull, increased risk of fractures even with minor trauma, joint pain and stiffness, hearing loss if the skull bones are affected, headaches due to skull bone enlargement, and in rare instances, nerve compression symptoms like numbness or tingling. However, it’s important to note that not everyone with Paget’s disease experiences symptoms, and the condition may be asymptomatic or discovered incidentally through medical tests or imaging. Early diagnosis and management are essential to prevent complications in those affected by this bone disorder.
difference between paget's disease and eczema
Paget’s disease of bone and eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, are distinct medical conditions with different underlying causes and characteristics. Paget’s disease of bone is a rare bone disorder characterized by abnormal bone remodeling, leading to bone deformities and pain. In contrast, eczema primarily affects the skin and is characterized by inflammation, itching, and a red rash. Paget’s disease of bone, or Paget’s disease, is unrelated to allergies, whereas eczema is often associated with allergic reactions and environmental triggers. These two conditions require different diagnostic approaches and treatment strategies. Paget’s disease of bone is typically managed with medications or surgery, whereas eczema is treated with topical creams, lifestyle modifications, and allergy management.
paget's disease treatment
Treatment for Paget’s disease aims to manage symptoms, reduce bone pain, and prevent complications. Medications like bisphosphonates are commonly prescribed to slow down the excessive bone remodeling process. In some cases, calcitonin or denosumab may also be used. Surgical intervention is considered if there are complications such as fractures, severe deformities, or nerve compression. Physical therapy can help improve mobility and alleviate discomfort. Regular monitoring through blood tests and imaging is essential to assess treatment effectiveness and prevent potential complications, with the goal of maintaining optimal bone health and function in individuals with Paget’s disease.
paget's disease of bone medication
Medications used for Paget’s disease of the bone primarily include bisphosphonates, such as alendronate, risedronate, or zoledronic acid. These drugs are prescribed to slow down the excessive bone remodeling process characteristic of Paget’s disease. By inhibiting bone resorption and turnover, bisphosphonates help reduce bone pain, prevent further deformities, and lower the risk of fractures. The choice of medication and dosing regimen will depend on the individual’s specific condition and the severity of their Paget’s disease. These medications are typically taken orally, and treatment duration can vary, often requiring ongoing monitoring and adjustments as necessary to ensure optimal bone health and symptom management.
The exact cause of Paget’s disease of bone is not fully understood, but there are several known risk factors that may increase the likelihood of developing the disease. Some of the most common risk factors for Paget’s disease of bone include:
1. Age: The risk of developing Paget’s disease of bone increases with age, with most cases diagnosed in people over the age of 55.
2. Genetics: There is a genetic component to Paget disease of bone, and having a family history of the disease increases the risk of developing it.
3. Viral infection: Some studies suggest that a viral infection, particularly a slow virus infection, may be a trigger for the development of Paget’s disease.
4. Gender: Men are more likely than women to develop Paget’s disease of bone.
5. Ethnicity: Paget’s disease of bone is more common in people of European descent.
6. Environmental factors: Exposure to certain environmental factors, such as toxins or radiation, may also increase the risk of developing Paget’s disease.
It’s important to note that having one or more of these risk factors does not necessarily mean that a person will develop Paget’s disease of bone. If you have concerns about your bone health or are at increased risk of developing Paget’s disease, it’s important to speak with your healthcare provider about appropriate screening and preventive measures.
In conclusion, Paget disease of the bone is a chronic and often asymptomatic skeletal disorder characterized by abnormal bone remodeling, which can lead to bone pain, deformities, fractures, and other complications. While its exact cause remains unclear, early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, such as bisphosphonates or, in severe cases, surgery, are essential for managing symptoms, preserving bone health, and preventing complications. Regular monitoring and individualized treatment plans are crucial to improving the quality of life for individuals with Paget’s disease, emphasizing the importance of prompt medical attention and ongoing care for those affected by this condition.
The cause of Paget disease of bone is unknown. Scientists suspect a combination of environmental and genetic factors contribute to the disease. Several genes appear to be linked to getting the disease.
Any of your bones can be affected by Paget’s disease. However, your pelvis, skull, spine and leg bones (femur and tibia) are most commonly affected by Paget’s disease. Paget’s disease can affect one bone (monoostotic) or many bones (polyostotic).
Blood and urine tests. The most important one for diagnosing Paget’s disease is a blood test for alkaline phosphatase, an enzyme made by bone. If the level of this enzyme is high, your doctor will want to do other tests. You might also need other tests, such as an MRI or a CT scan.
Medications. Osteoporosis drugs (bisphosphonates) are the most common treatment for Paget’s disease of bone. Bisphosphonates are typically given by injection into a vein, but they can also be taken by mouth.
The condition can affect one or multiple bones but the axial skeleton is most often involved (spine, pelvis, and skull). The condition does not spread to other bones but can progress in the preexisting site.
The bones most frequently affected are in the spine, skull, pelvis and lower legs. The exact cause of Paget’s disease is not known.
Fractures are common, especially hip fractures. Osteoporosis affects many bones. With Paget’s bone disease, there is an imbalance in the daily process of bone breakdown and buildup.
Knee replacement is a surgery to replace damaged parts of the knee joint with artificial ones. It’s recommended for severe arthritis or chronic knee pain. After …
Hip replacement is a surgical procedure to replace a damaged or worn-out hip joint with an artificial one. This procedure is typically recommended for individuals who have …
Elbow replacement is a surgical procedure to replace a damaged or worn-out elbow joint with an artificial one. This procedure is typically recommended for individuals who have …

Elbow replacement is a surgical procedure to replace a damaged or worn-out elbow joint with an artificial one. This procedure is typically recommended forindividuals who …

Shoulder replacement is a surgical procedure to replace a damaged or worn-out shoulder joint with an artificial one. This procedure is typically recommended for individuals who have …
Bunion surgery is a procedure to correct a bunion, which is a bony bump that forms on the joint at the base of the big toe. This bump can cause pain and discomfort, and make …
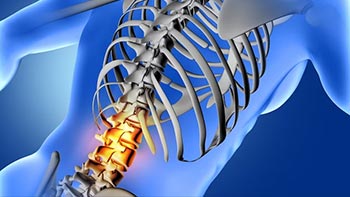
Disc hernia surgery is a procedure to treat a herniated disc, which occurs when the soft tissue inside the spinal disc pushes through a crack in the outer layer of the disc. This can …
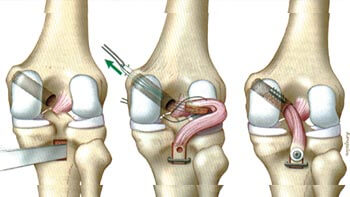
ACL and PCL reconstruction surgery is a procedure to repair a torn anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) or posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) in the knee. These ligaments help keep …
Knee osteotomy is a surgical procedure to treat knee arthritis by reshaping the bones in the knee joint. This procedure is typically recommended for individuals with early-stage arthritis who have …
Arthroscopic knee debridement is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that involves removing damaged tissue from the knee joint. This procedure is typically recommended for …
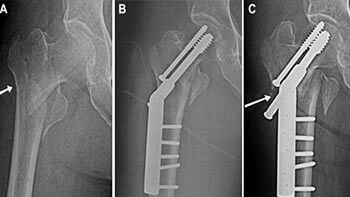
Hip nailing is a surgical procedure to treat a fractured hip by inserting a nail or rod into the femur bone to stabilize and support the hip joint. This procedure is typically recommended for …
Rehabilitation is a process of restoring physical, mental, and emotional health and function after an illness, injury, or surgery. The goal of rehabilitation is to help individuals regain independence, improve …
Laminectomy is a surgical procedure to relieve pressure on the spinal cord or nerves by removing part of the lamina, which is the bony covering of the spinal canal. This procedure is typically recommended for individuals with conditions such as spinal stenosis …
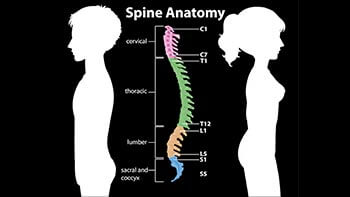
Spinal fusion is a surgical procedure to join two or more vertebrae together in the spine to stabilize the spine and reduce pain caused by conditions such as herniated discs, spinal stenosis, or scoliosis. During spinal fusion, the surgeon will use bone grafts, metal …

Meniscus repair is a surgical procedure to treat a torn meniscus, which is a piece of cartilage in the knee joint that acts as a shock absorber. This procedure is typically recommended for individuals with a meniscus tear caused by injury or degeneration. During …

Achilles tendon repair is a surgical procedure to treat a ruptured or torn Achilles tendon, which is the largest tendon in the body that connects the calf muscle to the heel bone. This injury is typically caused by sudden, forceful movements or overuse. During …


