The affordable cost of heart transplant surgery in iran
Best Hospital
We Introduce Best Hospital for General Heart Surgery
Best Doctors
We Introduce Best Doctors for General Heart Surgery
Best Price
We Try to introduce best Services with Regular Price



Heart Transplant Surgery
in Iran
Heart transplantation is a well-established procedure in Iran, with a long history of successful surgeries. Iran has been a pioneer in organ transplantation, including heart transplantation. The first successful heart transplant in Iran was performed in 1993, and since then, the country has made significant progress in the field.
Heart transplant surgeries are performed in specialized hospitals and medical centers in Iran. These centers have highly skilled and experienced medical staff, including surgeons, anesthesiologists, cardiologists, and other healthcare professionals who work together to ensure the success of the surgery.
Why Choose Iran for heart transplant surgery?
There are several reasons why Iran is a popular destination for heart transplant surgery. First, Iran has a well-established reputation for excellence in medical care and research, with highly skilled and experienced medical professionals who are trained to the highest standards. Second, the country has a well-organized organ donation program, which ensures a steady supply of donor hearts for transplant surgeries. Third, the cost of heart transplant surgery in Iran is significantly lower compared to many other countries, which makes it an attractive option for patients who may not be able to afford the procedure in their home country. Finally, Iran’s medical tourism infrastructure is well-developed, with modern hospitals, specialized clinics, and excellent accommodation options available to patients and their families.

Why Choose AriaMedTour?
IPD Tourism is a tourism company that specializes in organizing medical and tourism trips in Iran. There are several reasons to choose IPD Tourism:
1- Experience and competence: IPD Tourism has high experience and efficiency in the field of medical and tourist trips in Iran, because it works with a team of specialists and experts in this field.
2- Quality of service: IPD Tourism ensures quality services and comprehensive care for patients and visitors, as it provides quality services and seeks to meet the needs of customers in the best possible way.
3- Attention to details: IPD Tourism pays great attention to details and follows every step of the process of organizing and preparing the trip very carefully.
4- Economy: IPD Tourism seeks to provide the best solutions and services with competitive prices and according to customers’ budgets.
5- Effective communication: IPD tourism is characterized by effective and quick communication with customers, because they are provided with the necessary advice and support during the trip.

How much does Heart transplant surgery cost in Iran?
How much does Heart transplant surgery cost in Iran?
The cost of heart transplant surgery in Iran can vary depending on several factors, such as the patient’s medical condition, the hospital or medical center where the surgery is performed, and the specific treatment plan recommended by the medical team. However, in general, the cost of heart transplant surgery in Iran is significantly lower compared to many other countries.
According to recent estimates, the cost of heart transplant surgery in Iran can range from approximately $20,000 to $40,000, including hospitalization, medical tests, and follow-up care. This is considerably less expensive than the cost of the same procedure in many other countries, such as the United States, where the cost of heart transplant surgery can exceed $1 million.
HEART TRANSPLANT SURGERY IN IRAN: EVERYTHING YOU NEED TO KNOW
Heart transplant surgery in Iran is a well-established procedure that offers patients access to high-quality medical care, a reliable supply of donor hearts, and affordable costs. Before undergoing the procedure, patients undergo a thorough evaluation to determine their eligibility, and the medical team carefully matches the donor heart to the patient. The surgery itself typically takes several hours to complete and is followed by a period of hospitalization and close monitoring. Overall, heart transplant surgery in Iran can provide patients with a new lease on life and the opportunity to regain their health and quality of life.
IS IRAN THE RIGHT PLACE FOR HEART TRANSPLANT SURGERY?
Choosing Iran for heart transplant surgery can be a good option for patients who are seeking high-quality medical care, a reliable supply of donor hearts, and affordable costs. Iran has a well-established reputation for excellence in medical care and research, and its organ donation program is well-organized, which helps ensure a steady supply of donor hearts. In addition, the cost of heart transplant surgery in Iran is significantly lower compared to many other countries, making it a more accessible option for patients who may not be able to afford the procedure in their home country. Overall, Iran can be a good choice for patients seeking a safe, reliable, and cost-effective option for heart transplant surgery.
What is heart surgery?
Heart surgery refers to a variety of surgical procedures that are performed to treat heart conditions. These procedures can be performed either on the heart itself or on the blood vessels that supply the heart.
WHAT IS HEART TRANSPLANT SURGERY?
Heart transplant surgery is a complex surgical procedure that involves replacing a patient’s diseased or damaged heart with a healthy donor heart. The procedure typically takes several hours to complete and involves careful matching of the donor heart to the patient. After the surgery, patients typically require a period of hospitalization and close monitoring to ensure that the new heart is functioning properly and that there are no complications. Heart transplant surgery can be a life-saving procedure for patients with end-stage heart disease, allowing them to regain their health and quality of life.
WHY IS HEART TRANSPLANT DONE?
Heart transplant surgery is typically done in patients with end-stage heart disease, which is a condition where the heart is severely damaged and unable to function properly. This can be due to a range of underlying medical conditions, such as coronary artery disease, cardiomyopathy, or congenital heart defects. Heart transplant surgery is done to replace the patient’s diseased or damaged heart with a healthy donor heart, which can restore normal heart function and improve the patient’s quality of life. For many patients, heart transplant surgery is a life-saving procedure that allows them to regain their health and independence.

List of the best heart transplant surgeons
HEART TRANSPLANT TYPES
Heart transplant surgery can be performed in two main types: orthotopic heart transplant and heterotopic heart transplant. In orthotopic heart transplant, the patient’s diseased or damaged heart is removed and replaced with a healthy donor heart, while in heterotopic heart transplant, the donor heart is implanted alongside the patient’s existing heart. The type of heart transplant surgery recommended for a patient will depend on several factors, including the patient’s medical condition and overall health.
ARTIFICIAL HEART TRANSPLANT SURGERY
Artificial heart transplant surgery involves implanting a mechanical device that can replace the function of a patient’s diseased or damaged heart. This type of surgery may be recommended for patients who are not candidates for a traditional heart transplant or who are waiting for a suitable donor heart to become available. During the surgery, the artificial heart is connected to the patient’s blood vessels and other vital structures, and the patient’s own heart is removed or left in place. While artificial heart transplant surgery can be effective in restoring normal heart function and improving the patient’s quality of life, it is a complex procedure that requires careful selection of patients and close monitoring after surgery.
Artificial heart transplant pros and cons
Artificial heart transplant, also known as a total artificial heart implant, is a surgical procedure in which a person’s damaged or diseased heart is replaced with a mechanical device. Here are some pros and cons of artificial heart transplant:
Pros:
- Improved quality of life: An artificial heart transplant can significantly improve a patient’s quality of life, allowing them to perform daily activities that were previously difficult or impossible due to heart failure.
- Increased life expectancy: In some cases, an artificial heart transplant can increase a patient’s life expectancy by several years, giving them more time with their loved ones.
- No risk of rejection: Since the artificial heart is not made of human tissue, there is no risk of rejection by the patient’s immune system, unlike in a traditional heart transplant.
- Availability: Artificial heart transplants are more readily available than traditional heart transplants, which can be difficult to obtain due to a shortage of donor hearts.
Cons:
- Surgery risks: Like any surgical procedure, an artificial heart transplant carries some risks, including bleeding, infection, and blood clots.
- High cost: Artificial heart transplants can be very expensive, and may not be covered by insurance.
- Limited lifespan: The lifespan of an artificial heart is typically limited, and the device may need to be replaced after a few years.
- Mechanical failure: Mechanical failure of the artificial heart can occur, which can be life-threatening and require emergency surgery.
- Lifestyle changes: Patients with artificial heart transplants may need to make significant lifestyle changes, including taking medication and avoiding certain activities, to ensure the longevity of the device.
HEART TRANSPLANT ELIGIBILITY
Heart transplant eligibility depends on several factors, including the severity of the patient’s heart disease, their overall health, and their ability to tolerate the surgery and post-operative care. Generally, patients who have end-stage heart failure and have not responded to other treatments may be considered for a heart transplant. However, eligibility criteria may vary depending on the specific transplant center and the patient’s individual circumstances. A thorough evaluation, including medical tests and psychological assessments, is typically conducted to determine if a patient is a suitable candidate for a heart transplant.
HOW TO PREPARE FOR A HEART TRANSPLANT SURGERY
Preparing for a heart transplant surgery can be a lengthy and intensive process. Here are some general steps that a patient may take to prepare for a heart transplant surgery:
- Medical evaluation: The patient will undergo a thorough medical evaluation to determine if they are a suitable candidate for a heart transplant. This may involve various tests, such as blood tests, imaging tests, and heart function tests.
- Lifestyle changes: The patient may need to make lifestyle changes to improve their overall health and increase their chances of a successful transplant. This may include quitting smoking, losing weight, and/or increasing physical activity.
- Medication management: The patient will need to manage their medications closely and follow their doctor’s instructions regarding when and how to take them.
- Emotional support: The patient may benefit from emotional support from family, friends, or a mental health professional, as the process can be stressful and emotional.
- Preoperative preparations: In the weeks leading up to the surgery, the patient will need to follow specific instructions regarding diet, exercise, and medication use. They may also need to fast for a certain period before the surgery.
- Postoperative care: The patient should plan for postoperative care, including arranging for someone to help them at home, scheduling follow-up appointments with their doctor, and understanding the signs of potential complications.
Blood matching in a heart transplant surgery
Blood matching is an important factor in a successful heart transplant surgery. A heart transplant recipient’s blood type must be compatible with the blood type of the donor heart. The ABO blood group system is used to determine blood compatibility between the donor and recipient.
In addition to blood type, other factors such as tissue matching and cross-matching are also considered to reduce the risk of organ rejection. Tissue matching involves testing the recipient’s blood for certain proteins that are present on the surface of cells throughout the body, including the heart. Cross-matching involves testing the recipient’s blood against the donor’s blood to ensure that there are no antibodies that could lead to rejection.
Matching blood and tissue types as closely as possible between the donor and recipient can increase the chances of a successful transplant and reduce the risk of rejection. However, even with a good match, the recipient may still require lifelong immunosuppressive therapy to prevent rejection of the transplanted heart. Close monitoring and follow-up care are also essential for a successful heart transplant outcome.
Tissue typing and compatibility
Tissue typing and compatibility are important considerations in a successful heart transplant surgery. Tissue typing involves analyzing the proteins on the surface of cells, known as human leukocyte antigens (HLAs), to determine the compatibility between the donor and recipient.
HLAs play a crucial role in the immune system and help the body distinguish between its own tissues and foreign tissues. In heart transplantation, a close match between the donor and recipient’s HLA types can help reduce the risk of rejection.
In addition to HLA matching, other factors such as blood type and the presence of antibodies in the recipient’s blood are also considered when evaluating donor-recipient compatibility. A thorough evaluation and testing process is typically conducted to identify potential matches and minimize the risk of rejection


Diseases related to heart transplant
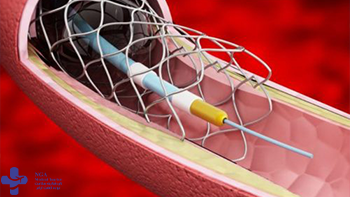
Angiography
Coronary angiography is a procedure that uses a special dye (contrast material) and x-rays to see how blood flows through the arteries in your heart.
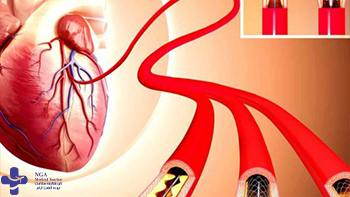
Angioplasty
Angioplasty is a procedure used to open blocked coronary arteries caused by coronary artery disease.
Heart Bypass Surgery
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) refers to a group of conditions that affect the heart and blood vessels. These conditions can include coronary artery disease (CAD), heart failure,arrhythmias, heart valve problems, and peripheral artery disease, among others.
Coronary artery disease (CAD)
Transplant recipients are at increased risk of developing CAD, which is the buildup of plaque in the arteries that supply blood to the heart. CAD can lead to angina, heart attack, or other complications.
Heart surgery
Heart surgery refers to a variety of surgical procedures that are performed to treat heart conditions. These procedures can be performed either on the heart itself or on the blood vessels that supply the heart.
Aortic Aneurysm Surgery
Aneurysm surgery is a treatment for aortic aneurysms. A surgeon removes the damaged part of your aorta and replaces it with a synthetic fabric tube called a graft. The surgery is very effective when performed before aneurysm rupture. Recovery for most people includes five to 10 days in the hospital and four to six weeks at home
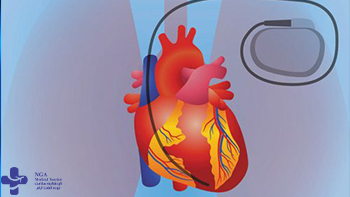
Heart Pacemaker Surgery
A permanent pacemaker is a small electronic device that helps your heart maintain a regular, healthy rhythm. It’s implanted in your chest to regulate electrical problems with the heart, such as beating too quickly or too slowly.
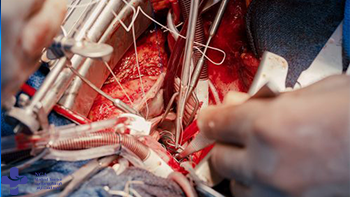
Open Heart Surgery
Open-heart surgeries treat heart problems including heart failure, congenital heart defects, arrhythmias, aneurysms and coronary artery disease. During the procedure, a surgeon cuts through the breastbone and spreads the ribcage to access the heart. Open-heart surgery may include CABG (bypass surgery), heart transplant and valve replacement.
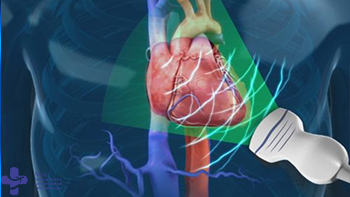
Echo
A heart echo, also known as an echocardiogram, is a diagnostic test that uses ultrasound waves to create images of the heart. This test is used to evaluate the structure and function of the heart, and can help diagnose a variety of heart conditions.
Heart transplant surgery hospital in iran

Pars hospital
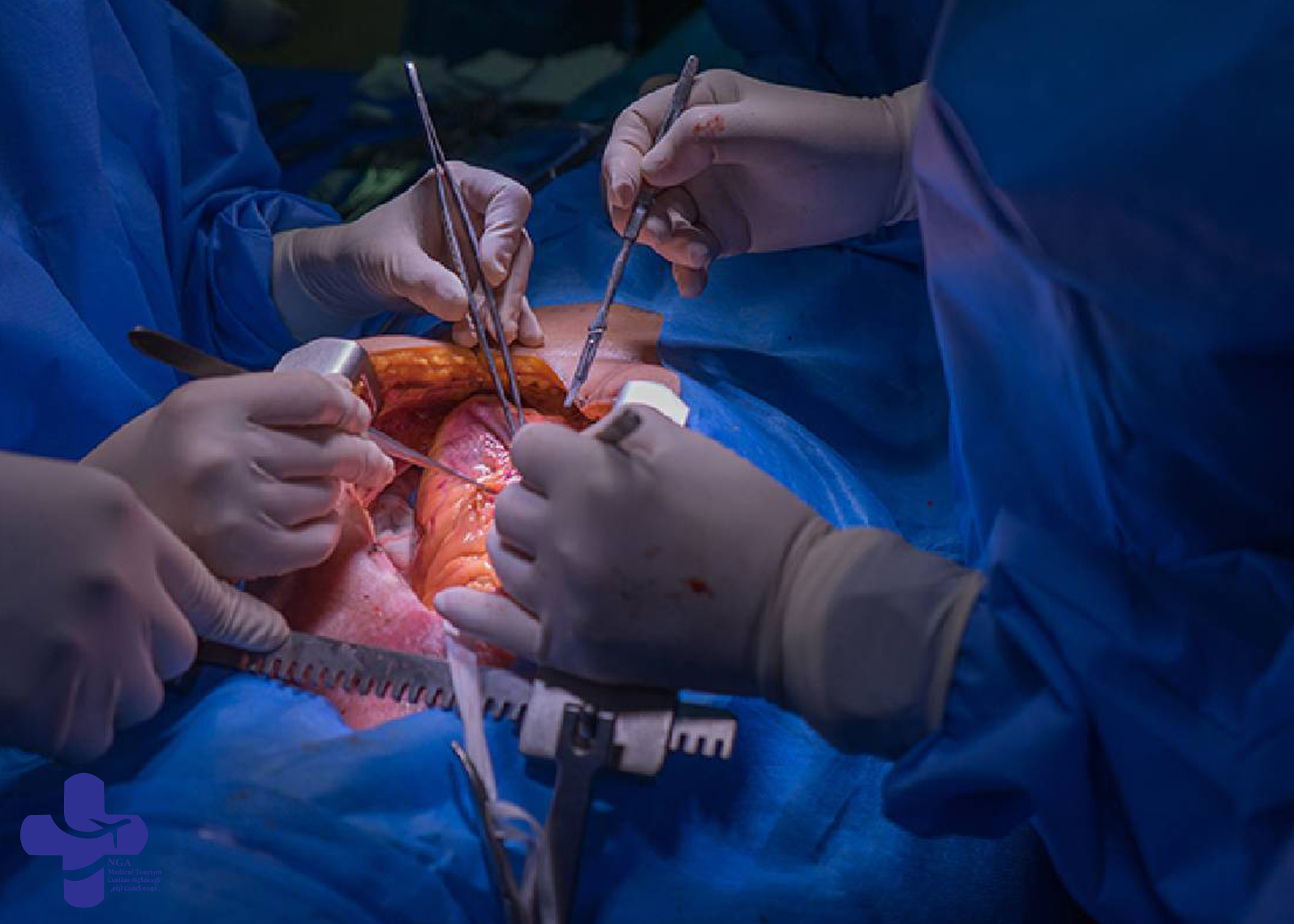
HOW HEART TRANSPLANT SURGERY IS PERFORMED?
Heart transplant surgery is a complex and intricate procedure that typically takes several hours to complete. Here are the general steps involved in a heart transplant surgery:
- Anesthesia: Before the surgery, the patient is given general anesthesia to ensure they are unconscious and do not feel any pain during the procedure.
- Incision: The surgeon makes an incision in the patient’s chest to access the heart. The sternum is then separated to provide access to the heart.
- Removal of the diseased heart: The surgeon carefully removes the patient’s diseased heart while ensuring that the surrounding blood vessels are not damaged.
- Preparation of the donor heart: The donor heart is removed from the donor’s body and transported to the recipient’s hospital. The heart is then prepared for transplantation, which may involve removing excess tissue and connecting the blood vessels.
- Implantation of the donor heart: The surgeon carefully implants the donor heart in the recipient’s chest, connecting it to the blood vessels and ensuring that it is functioning properly.
- Closing the incision: Once the heart is successfully implanted, the surgeon closes the incision with sutures or staples.
- Recovery: The patient is closely monitored in the intensive care unit (ICU) for several days following the surgery. They will receive medication to prevent rejection of the transplanted heart and other treatments as needed.
- Follow-up care: The patient will need to attend regular follow-up appointments with their transplant team and take medication to prevent rejection for the rest of their life. They will also need to make lifestyle changes and avoid activities that could put stress on the heart.
AFTER THE HEART TRANSPLANT SURGERY
After a heart transplant surgery, the patient will require close monitoring and follow-up care to ensure that the transplanted heart is functioning properly and to prevent rejection. Here are some general considerations for the post-operative period:
- Recovery period: The patient will spend several days in the hospital recovering from the surgery. They may need to stay in the intensive care unit (ICU) for a period of time before being transferred to a regular hospital room.
- Medications: The patient will need to take a variety of medications to prevent rejection of the transplanted heart. These medications suppress the immune system and help the body accept the new organ.
- Lifestyle changes: The patient will need to make significant lifestyle changes, including following a heart-healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and avoiding activities that could put stress on the heart.
- Follow-up appointments: The patient will need to attend regular follow-up appointments with their transplant team to monitor the function of the transplanted heart and adjust medications as needed.
- Emotional support: The patient may benefit from emotional support from family, friends, or a mental health professional, as the process can be stressful and emotional.
- Potential complications: The patient should be aware of the signs of potential complications, such as infection, rejection, or problems with the transplanted heart, and seek medical attention promptly if any symptoms arise.
- Long-term care: The patient will need to continue taking immunosuppressive medications for the rest of their life and will need ongoing follow-up care with their transplant team to ensure the long-term success of the transplant.
What to do when you are home?
After being discharged from the hospital following a heart transplant surgery, the patient will need to follow a strict regimen of self-care and monitoring to ensure the success of the transplant. Here are some general guidelines for what to do when you are home:
- Follow medication instructions: It is important to take all medications exactly as prescribed by your doctor. Do not skip doses or stop taking medications without first consulting your transplant team.
- Monitor vital signs: Check your blood pressure, heart rate, and temperature regularly, and report any significant changes to your transplant team.
- Watch for signs of infection: Be vigilant for signs of infection, such as fever, chills, redness, or swelling, and report any symptoms to your transplant team immediately.
- Attend follow-up appointments: Attend all follow-up appointments with your transplant team, including regular blood tests and heart function tests.
- Follow a healthy diet: Eat a heart-healthy diet that is low in saturated fats, cholesterol, and salt. Avoid alcohol and tobacco products.
- Exercise regularly: Engage in regular physical activity as recommended by your transplant team, such as walking or light aerobic exercise.
- Manage stress: Practice stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
- Be aware of potential complications: Be aware of the signs of potential complications, such as rejection, infection, or problems with the transplanted heart, and seek medical attention promptly if any symptoms arise.
- Stay in communication with your transplant team: Keep in touch with your transplant team and report any significant changes in your health or well-being. They can provide guidance and support as needed.
By following these guidelines and staying in close communication with your transplant team, you can help ensure the long-term success of your heart transplant.
LIFE EXPECTANCY AFTER HEART TRANSPLANT
Life expectancy after a heart transplant varies depending on several factors, including the patient’s age, overall health, and the success of the transplant. Generally, heart transplant recipients have a good long-term prognosis, with an average survival rate of about 85% at one year after the transplant, 75% at five years, and 55% at ten years.
Heart transplant rejection
Heart transplant rejection occurs when the body’s immune system recognizes the transplanted heart as foreign and attacks it. This can cause damage to the heart tissue and impair its function.
Heart transplant rejection rate
The rejection rate after heart transplant can vary depending on several factors, including the patient’s age, overall health, and the success of the transplant. With current immunosuppressive medications, the incidence of acute rejection has decreased significantly. According to the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT), the one-year survival rate after heart transplant is approximately 85%, and the five-year survival rate is approximately 75%.
Heart transplant rejection symptoms
Heart transplant rejection can cause a variety of symptoms, which can vary depending on the type and severity of the rejection. Here are some common symptoms of heart transplant rejection:
- Acute rejection: Symptoms of acute rejection may include fatigue, shortness of breath, rapid or irregular heartbeat, fever, chest pain, and swelling or tenderness around the incision site. Some patients may also experience flu-like symptoms, such as headache, nausea, and muscle aches.
- Chronic rejection: Symptoms of chronic rejection may include fatigue, shortness of breath, swelling in the legs or abdomen, weight gain, and decreased exercise tolerance. Patients may also experience irregular heartbeats, decreased urine output, and a general feeling of being unwell.
HEART TRANSPLANT COMPLICATIONS
Heart transplant surgery is a complex procedure that carries certain risks and potential complications. Some of the possible complications include:
- Rejection: The most common complication after a heart transplant is rejection, which occurs when the body’s immune system attacks the transplanted heart. Symptoms of rejection may include fever, fatigue, shortness of breath, and swelling.
- Infection: Patients who have received a heart transplant are at an increased risk of infection due to the immunosuppressive medications they must take to prevent rejection. Infections can be serious and require prompt medical attention.
- Complications from medications: The medications used to prevent rejection can cause side effects and complications, such as high blood pressure, kidney damage, and increased risk of infection.
- Cardiac allograft vasculopathy: This is a condition that can occur years after a heart transplant, in which the blood vessels in the transplanted heart become narrowed and blocked, leading to reduced blood flow to the heart.
5. Other complications: Other possible complications of heart transplant surgery include bleeding, blood clots,
THE COST OF HEART TRANSPLANT SURGERY IN IRAN
The cost of heart transplant surgery in Iran can vary depending on several factors, including the hospital or medical center where the surgery is performed, the patient’s medical needs, and the duration of hospital stay. However, heart transplant surgery in Iran is generally more affordable than in many other countries.
According to recent estimates, the cost of heart transplant surgery in Iran ranges from $40,000 to $60,000, which includes hospitalization, transplantation surgery, and post-operative care. This cost may or may not include pre-operative evaluation and diagnostic testing.
HEART TRANSPLANT AFTERCARE AND RECOVERY
The cost of heart transplant surgery in Iran can vary depending on several factors, including the hospital or medical center where the surgery is performed, the patient’s medical needs, and the duration of hospital stay. However, heart transplant surgery in Iran is generally more affordable than in many other countries.
According to recent estimates, the cost of heart transplant surgery in Iran ranges from $40,000 to $60,000, which includes hospitalization, transplantation surgery, and post-operative care. This cost may or may not include pre-operative evaluation and diagnostic testing.
It is important to note that insurance coverage for heart transplant surgery in Iran may vary depending on the patient’s insurance plan and coverage.
HEART TRANSPLANT AFTERCARE AND RECOVERY
Here are a few general considerations for heart transplant aftercare and recovery:
Medication management: Patients will need to take immunosuppressive medications for the rest of their life to prevent rejection of the transplanted heart.
Follow-up appointments: Patients will need to attend regular follow-up appointments with the transplant team to monitor the function of the transplanted heart and adjust medications as needed.
Lifestyle changes: Patients will need to make significant lifestyle changes, including following a heart-healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and avoiding activities that could put stress on the heart.
Emotional support: Patients may benefit from emotional support from family, friends, or a mental health professional, as the process can be stressful and emotional.
Potential complications: Patients should be aware of the signs of potential complications, such as infection, rejection, or problems with the transplanted heart, and seek medical attention promptly if any symptoms arise.
Long-term care: Patients will need to continue taking immunosuppressive medications for the rest of their life and will need ongoing follow-up care with their transplant team to ensure the long-term success of the transplant.
Your message will be reviewed by our doctors and specialist . We will get back to you within 24 Hours.
Nodeh Gasht Aram experts will answer your questions 24/7 , through online chat or by phone.
You get medical opinion and cost estimate
Nodeh Gasht Aram plan your trip.
We arrange your medical visa , flight, ticket, appointments, accommodation etc.
Booking various types of accommodation
interpreter
insurance
SIM & Internet
City Tour
Collaboration with different medical centers to get the best diagnosis and treatment by talent doctors and surgeons...
Post-treatment recuperation and check up .
After the completion of treatment and you return to your country, we will follow you around the clock.
Why Nodeh Gasht Aram?
- Contact Us Via Whatsapp: Your message will be reviewed by our doctors and specialist . We will get back to you within 24 Hours.
- Free Consultation: Nodeh Gasht Aram experts will answer your questions 24/7, through online chat or by phone.
- Qoutation: You get medical opinion and cost estimate
- Ticketing & Visa Support: Nodeh Gasht Aram plan your trip We arrange your medical visa , flight, ticket, appointments, accommodation etc.
- Hotel Booking,Travel Insurance,Interpreter: Booking various types of accommodation, interpreter, insurance, SIM & Internet, City Tour
- Hospitality & Diagnosis & Treatment: Collaboration with different medical centers to get the best diagnosis and treatment by talent doctors and surgeons.
- Recovery: Post-treatment recuperation and check up .
- Follow-up: After the completion of treatment and you return to your country, we will follow you around the clock.
Price list of diseases related to heart transplant surgery
No | The name of the disease | price |
|---|---|---|
1 | Open heart surgery (CABG) | About 8000$ |
2 | Vessel angioplasty (one vessel) surgery | About 2500$ |
3 | Aortic valve or mitral valve replacement | About 8000$ |
4 | PCI stent and ballooning of coronary arteries | About 4500$ |
5 | Echocardiography | About 100$ |
6 | Ventricular septal defects (VSD) repair | About 7000$ |
7 | Atrial septal defect (ASD) repair | About 7000$ |
8 | EPS ablation | About 3000 |

Heart transplant diet
After a heart transplant, it is important for patients to follow a heart-healthy diet to help maintain optimal health and prevent complications. Here are some general guidelines for a heart transplant diet:
- Low-fat foods: Patients should aim to eat a diet that is low in saturated and trans fats, which can contribute to heart disease. Good options include lean protein sources, such as fish and poultry, and plant-based fats, such as olive oil and nuts.
- High-fiber foods: A diet that is high in fiber can help lower cholesterol levels and improve heart health. Good sources of fiber include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes.
- Limited sodium: Patients should aim to limit their sodium intake to no more than 2,300 milligrams per day. This can help lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of heart disease. Patients should avoid processed foods and opt for fresh, whole foods instead.
- Limited sugar: A diet that is high in sugar can contribute to weight gain and increase the risk of heart disease. Patients should limit their intake of sugary foods and drinks and opt for natural sweeteners, such as fruit.
- Balanced meals: Patients should aim to eat balanced meals that include a variety of nutrient-dense foods, such as lean protein, whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.

Heart transplant exercise
Exercise is an important part of the recovery process after a heart transplant. Regular physical activity can help improve cardiovascular health, increase strength and endurance, and reduce the risk of complications. Here are some general guidelines for exercise after a heart transplant:
- Start slowly: Patients should start with light exercise, such as walking or cycling, and gradually increase the duration and intensity of their workouts over time.
- Follow a structured exercise program: Patients should work with their transplant team and a certified exercise specialist to develop a structured exercise program that is tailored to their individual needs and goals.
- Monitor heart rate and blood pressure: Patients should monitor their heart rate and blood pressure during exercise and adjust the intensity as needed to stay within a safe range.
- Avoid high-impact activities: Patients should avoid high-impact activities that could put stress on the heart, such as contact sports or weightlifting.
- Stay hydrated: Patients should drink plenty of fluids before, during, and after exercise to prevent dehydration.
- Listen to the body: Patients should pay attention to how their body feels during exercise and stop if they experience any chest pain, shortness of breath, or other symptoms.
- Be consistent: Patients should aim to exercise regularly, ideally at least 30 minutes a day, five days a week, to maintain cardiovascular health and improve overall fitness.
HEART TRANSPLANT AND QUALITY OF LIFE
Heart transplant surgery will have a great impact on your quality of life. There will be some changes.
Heart transplant and immunosuppressants
After a heart transplant, patients require immunosuppressive medications to prevent the body from rejecting the transplanted heart. These medications work by suppressing the immune system, which reduces the risk of rejection but also increases the risk of infection and other complications.
Immunosuppressive medications are typically prescribed in combination and may include:
- Calcineurin inhibitors: These medications, such as cyclosporine and tacrolimus, are often used as the backbone of immunosuppression therapy after heart transplantation.
- Antiproliferative agents: These medications, such as mycophenolate and azathioprine, work by preventing the proliferation of immune cells that can lead to rejection.
- Steroids: Corticosteroids, such as prednisone, can reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system.
- Biologic agents: These medications, such as basiliximab and alemtuzumab, target specific immune cells to prevent rejection.
It is important for patients to take these medications exactly as prescribed by their transplant team to prevent rejection and minimize the risk of complications. Patients will need to have regular blood tests to monitor medication levels and kidney function, as these medications can have side effects such as high blood pressure, kidney damage, and increased risk of infection.
Patients who take immunosuppressive medications after a heart transplant will need to follow certain precautions to reduce the risk of infection, such as avoiding contact with sick individuals and practicing good hygiene. It is also important for patients to report any symptoms of infection or rejection to their transplant team promptly.

Exercises after heart transplant surgery
Exercise is an important part of the recovery process after a heart transplant. Regular physical activity can help improve cardiovascular health, increase strength and endurance, and reduce the risk of complications. Here are some general guidelines for exercise after a heart transplant:
- Start slowly: Patients should start with light exercise, such as walking or cycling, and gradually increase the duration and intensity of their workouts over time.
- Follow a structured exercise program: Patients should work with their transplant team and a certified exercise specialist to develop a structured exercise program that is tailored to their individual needs and goals.
- Monitor heart rate and blood pressure: Patients should monitor their heart rate and blood pressure during exercise and adjust the intensity as needed to stay within a safe range.
- Avoid high-impact activities: Patients should avoid high-impact activities that could put stress on the heart, such as contact sports or weightlifting.
- Stay hydrated: Patients should drink plenty of fluids before, during, and after exercise to prevent dehydration.
- Listen to the body: Patients should pay attention to how their body feels during exercise and stop if they experience any chest pain, shortness of breath, or other symptoms.
- Be consistent: Patients should aim to exercise regularly, ideally at least 30 minutes a day, five days a week, to maintain cardiovascular health and improve overall fitness.
Smoking and consuming alcohol
it is generally recommended that heart transplant recipients avoid smoking and consuming alcohol as much as possible after their surgery. Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can increase the risk of complications, including infection, rejection, and damage to the transplanted heart. It is important for heart transplant recipients to follow the guidance of their transplant team regarding lifestyle choices, including smoking and alcohol consumption
Sex and pregnancy after heart transplant surgery
After heart transplant surgery, patients may have questions about sex and pregnancy. Here are some general considerations:
- Sex: Patients can typically resume sexual activity after their transplant once their incision has healed and they have received clearance from their transplant team. It is important to discuss any concerns with the transplant team, as some medications used after a transplant can affect sexual function.
- Pregnancy: Women who have had a heart transplant should discuss their plans for pregnancy with their transplant team. Pregnancy after a heart transplant can be high-risk and requires careful monitoring. It is generally recommended that women wait at least one year after their transplant before becoming pregnant, and that they work closely with their transplant team and an obstetrician throughout their pregnancy.
3. Contraception: Patients who are sexually active and do not wish to become pregnant should use contraception to prevent unwanted pregnancy. It is important to discuss contraceptive options with the transplant team, as some medications used after a transplant can interact with certain types of contraception
Working and driving after heart transplant surgery
After heart transplant surgery, patients may have questions about when they can return to work and driving. Here are some general guidelines:
- Work: The timing of returning to work after heart transplant surgery depends on the type of work and the individual’s recovery progress. Patients with physically demanding jobs may need to take more time off than those with desk jobs. Patients should discuss their return to work with their transplant team, who can provide individualized guidance based on each patient’s needs.
- Driving: Patients should not drive for at least six weeks after their heart transplant surgery, or until their transplant team gives them clearance to do so. Patients may need to undergo a driving evaluation before they are cleared to drive. It is important to discuss any concerns about driving with the transplant team.
Conclusion
You can contact IPD Tourism if you want to have heart transplant surgery in Iran. IPD Tourism will help you and take care of everything for you. By everything we mean the treatment, selecting the best doctors and surgeons, online consultation, and many more thing including the visa to Iran, the transportation, the hotels, picking you up from the airport and driving you back when you leave and assigning a personal assistant and interpreter to accompany you during your treatment.
After the surgery IPD Tourism will provide free online follow-up and post-hospitalization health care even after you go back home. You can fill the form in this page or contact IPD Tourism on WhatsApp to arrange for you heart transplant surgery in Iran
Frequently Asked Questions
A heart transplant surgery is a medical procedure in which a patient’s diseased or damaged heart is replaced with a healthy donor heart.
Eligibility for a heart transplant surgery depends on several factors, such as the severity of the heart disease, the overall health of the patient, and the availability of a suitable donor heart. A heart transplant is usually considered for patients with end-stage heart failure who have exhausted other treatment options.
A heart transplant surgery usually takes between 4 to 6 hours, although it can take longer depending on the complexity of the case.
The recovery period after a heart transplant surgery can vary depending on the individual case, but it typically involves a hospital stay of several weeks to monitor the patient’s progress and manage any complications. After discharge, the patient will need to attend regular follow-up appointments and take immunosuppressive medications for the rest of their life.
As with any major surgery, there are risks associated with a heart transplant surgery, including bleeding, infection, rejection of the donor heart, and complications from the use of immunosuppressive medications. However, with proper medical care and follow-up, many patients go on to lead long and healthy lives after a heart transplant surgery.
The lifespan of a transplanted heart can vary depending on several factors, such as the age and health of the donor heart, the age and health of the recipient, and the effectiveness of the immunosuppressive medications. On average, a transplanted heart can last for 10 to 15 years, although some patients have lived with their transplanted hearts for more than 20 years.
Heart transplant recipient survival rates vary based on a number of factors. A 2014 report by the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network and the Scientific Registry of Transplant Recipients stated that the overall survival rate in the U.S. is about 88 percent after one year and about 75 percent after five years.
It is done when there are no other options left, and the patient will die from heart disease without a donor heart. Transplant surgery is risky, but for these patients, death is certain without a new heart.
Donors for heart transplants are individuals who may have recently died or become brain dead, which means that although their body is being kept alive by machines, the brain has no sign of life. Many times, these donors died as a result of a car accident, severe head injury, or a gunshot wound
The world’s longest-surviving heart transplant patient has died, 33 years after his life-saving operation. John McCafferty was told he had only five years to live when he received the transplant at Harefield Hospital in west London, on 20 October 1982.
How long is the waiting list? Unfortunately, the waiting times for heart transplants are long — often more than six months. Each patient on our waiting list returns for an outpatient visit to our transplant clinic every two to three months, or more frequently if necessary.
For heart transplants, the gender difference was found only among men who received organs donated by females. The study found men who received female hearts were 13% more likely to lose the heart compared to those who got male-donated organs.
Generally speaking, a heart transplant before insurance coverage can potentially cost well over 1 million dollars. Some but not all of what patients pay for includes: Initial testing with or without hospitalization. The surgery and hospital stay afterward.
Though a successful heart transplant was a major medical milestone, in the early days, patients with these new hearts didn’t live that long. Now many people live for decades, with a median survival of 14 years, according to Dr
Survival — Approximately 85 to 90 percent of heart transplant patients are living one year after their surgery, with an annual death rate of approximately 4 percent thereafter. The three-year survival approaches 75 percent.
Setting complications aside, Newark Beth Israel heart transplant enables most patients to return to a normal life— the majority of patients can resume all normal daily activities and live with minimal to no symptoms. Heart transplant patients can take control of their recovery and heart transplant life expectancy
“Actually, it is not unusual for someone who receives a heart transplant at a relatively young age to need a second transplant,” said Mark J. Zucker, MD, JD, Director of the Heart Failure Treatment and Transplant Program. “Heart disease can develop for many reasons that we cannot predict.”
All people fit into one of four blood types — A, B, AB and O. Everyone is compatible with some blood types but not all of them as follows: People with blood type A are compatible with donor organs (or blood) from a person with type A or O blood. People with blood type B are compatible with blood type B or O.
Moderate drinking after the surgery is allowed but it is recommended to wait for a month or two before drinking.
There is no lower age limit for heart transplant surgery. You just need to find a heart that matches the patient blood type and tissues.