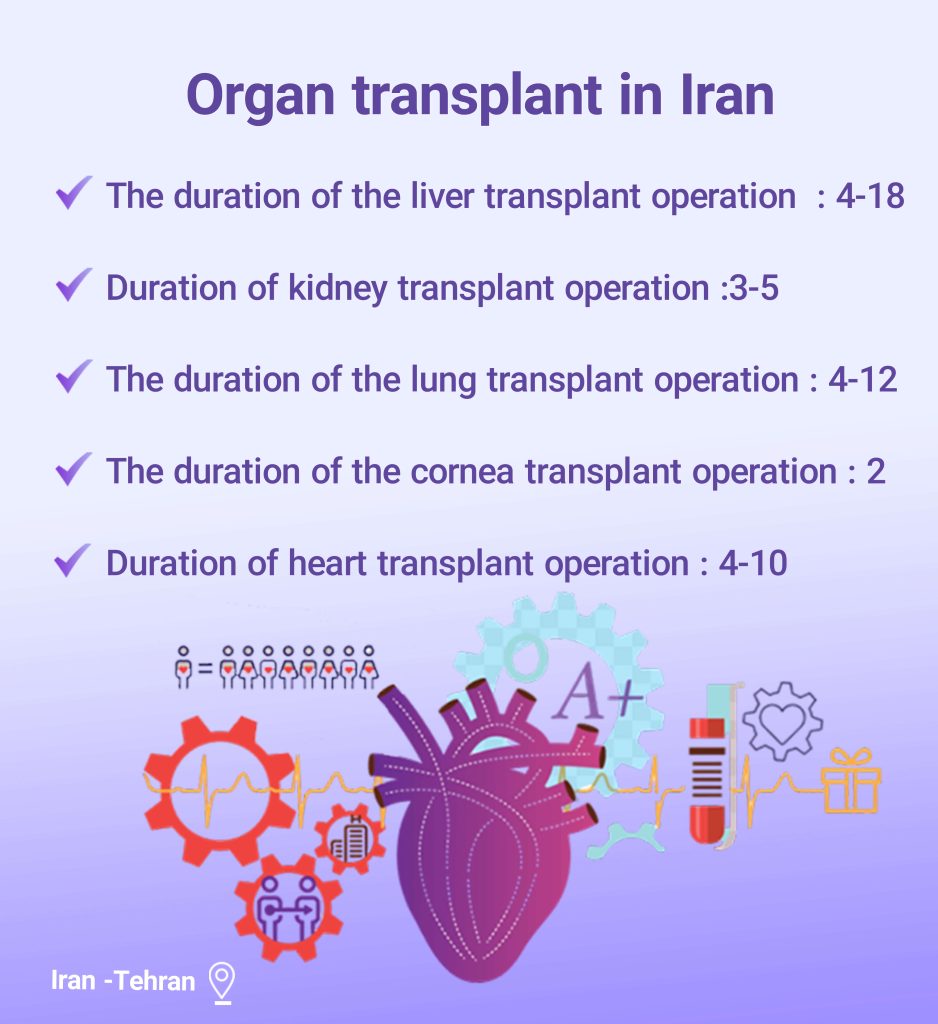
Organ Transplantation in Iran: No Waiting List
Organ transplantation stands as a beacon of hope, a medical breakthrough that has revolutionized healthcare worldwide. The intricate dance of donor and recipient, orchestrated by skilled medical professionals, has the power to transform lives in profound ways.
In the realm of Organ Transplantation, precision is paramount. The process involves the meticulous matching of donors and recipients, ensuring compatibility at the molecular level. This personalized approach not only enhances the success rates of transplants but also reduces the risk of postoperative complications.
Organ Transplantation represents a triumph of medical science over adversity. It is a testament to human resilience and the relentless pursuit of innovation in the face of life-threatening conditions. Patients who once faced uncertain futures now have the opportunity for a second chance at life, thanks to the miracles performed through organ transplants.
As we delve into the significance of Organ Transplantation, we witness a symphony of collaboration between medical professionals, donors, and recipients. This collaborative spirit extends beyond borders, transcending cultural and geographical boundaries in the pursuit of a common goal: saving lives.
In the context of this transformative medical procedure, Iran emerges as a noteworthy player. The country has made substantial strides in Organ Transplantation, exemplifying a commitment to excellence in healthcare. Iranian medical facilities boast cutting-edge technology and a comprehensive regulatory framework, ensuring the highest standards of ethical practice.
Iran’s contributions to the field of Organ Transplantation resonate globally. The nation serves as an inspiration, illustrating what can be achieved when dedication, expertise, and compassion converge. As we look towards the future of healthcare, Iran’s impact on the landscape of organ transplantation is undeniable, echoing across continents and offering hope to those in need.
How is organ transplantation done in Iran? Is kidney transplant done in Iran? How is a kidney transplant in Iran for foreigners? How much does a kidney transplant cost in Iran? Which is the best transplant hospital in Iran? Stay with us to answer these questions and more.
What is organ transplantation?
Organ transplantation is a complex and life-saving medical procedure that has revolutionized the treatment of various organ failures and diseases.
This comprehensive process encompasses vital organs such as the heart, lungs, liver, kidneys, pancreas, and small intestine, along with tissues like corneas, skin, bone, and bone marrow. In this intricate procedure, an organ or tissue from a donor is surgically implanted into a recipient, serving as a critical intervention to replace a malfunctioning or failed organ. It acts as a lifeline for individuals grappling with severe organ-related health conditions.
Medical Tourism in Iran is a online medical tourism platform that you can find the best general surgeons in Iran. The general cost of surgery in Iran may vary from person to person and may be determined by the physician depending on the disease or beauty. So if you have a general surgery in Iran, you can contact us and get free Iran consultation.You can call the following numbers for a free consultation:+989120131750 – +9891201317501 – +989129369336
Organ Donation Facts
Organ Transplantation
heart transplant surgery
types of organ transplantation:
Here are some of the common types of organ transplantation:
Kidney transplantation is one of the most common types of organ transplantation. It involves the transplantation of a healthy kidney from a living or deceased donor into a recipient with kidney failure or severe kidney disease.
Liver transplantation becomes necessary when a recipient is grappling with end-stage liver disease, cirrhosis, or acute liver failure. This procedure involves the transplantation of either the entire liver or a portion of it, sourced from either a living or deceased donor.
Heart transplantation is undertaken for individuals facing severe heart failure or heart-related conditions. This intricate procedure involves transplanting a healthy heart from a deceased donor into the recipient to restore cardiac function.
Lung Transplantation in Iran
The transplantation of lungs is carried out in cases of end-stage lung diseases, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or pulmonary fibrosis. It involves the replacement of one or both lungs, depending on the recipient’s condition.
Pancreas Transplantation in Iran
Pancreas transplantation is commonly undertaken for individuals experiencing complications related to type 1 diabetes. This procedure can be coupled with a kidney transplant, known as a simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplant, or performed independently as an isolated pancreas transplant.
Intestine Transplantation in Iran
Intestine transplantation is rare and is usually performed in cases of intestinal failure or certain gastrointestinal disorders. It can involve the transplantation of the small intestine, large intestine, or both.
Cornea Transplantation in Iran
Cornea transplantation, also known as keratoplasty, is a common procedure to restore vision in individuals with corneal damage or disease. A healthy cornea from a donor replaces the damaged cornea.
Bone Marrow or Stem Cell Transplantation in Iran
This procedure is frequently employed in the treatment of diverse blood disorders like leukemia, lymphoma, and aplastic anemia. The transplantation involves replacing diseased or damaged bone marrow with healthy bone marrow or stem cells.
Skin Transplantation
The treatment of severe burns, chronic non-healing wounds, or skin disorders often involves the use of skin grafts or transplants. Skin can be sourced either from the patient’s own body (autograft) or from a donor (allograft).
Hand or Limb Transplantation in Iran
Limb transplantation, a sophisticated procedure, aims to reinstate upper or lower limb functionality for those who’ve lost limbs either through traumatic injury or congenital conditions.
What are the pros and cons of organ transplantation?
Pros
- Life-SavingImproved
- Quality of Life
- Long-Term Survival
- Medical Advances
- Treatment for Various Organs
Cons
- Risk of Rejection
- Surgical Risks
- Cost
- Long-Term Monitoring
- Immunosuppression
What is the method of collecting stem cells for transplants in Iran?

Stem cell collection for autologous transplantation
In the case of a planned transplant using your own stem cells (autologous transplantation), the process involves a technique called apheresis to gather blood stem cells.
Before apheresis, daily injections of growth factors are administered to boost stem cell production and facilitate their migration into the bloodstream for collection.
In the apheresis procedure, blood is withdrawn from a vein and directed through a device that separates it into various components, including stem cells. These collected stem cells are then frozen for future use in transplantation. The remaining blood is returned to your body during this process.
Stem cell collection for allogeneic transplantation
If you are transplanting using donor stem cells (allogeneic transplantation), you will need a donor. When a donor is found, stem cells are collected from that person for transplantation.
Stem cells can come from the blood or bone marrow of your donor. Your transplant team will decide which one is best for you based on your situation.
Another type of allogeneic transplant uses umbilical cord blood stem cells (umbilical cord blood transplants). Mothers can donate a umbilical cord after the birth of their baby. The blood from this umbilical cord is frozen and stored in the umbilical cord blood bank until it is needed for a bone marrow transplant.
Organ transplant experiences in Iran
History of organ transplantation in Iran
These milestones in organ transplantation showcase the pioneering efforts of Iranian medical professionals:
- In 1991, Dr. Ghavamzadeh initiated the first bone marrow transplant in Iran, marking a significant stride in medical advancements.
- Dr. Ahmadi achieved the first successful lung transplant in 2000 at Imam Khomeini Hospital, Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
- Shiraz Namazi Hospital witnessed the first successful kidney transplant in Iran in 1347, performed by a live donor.
- Dr. Shams conducted the inaugural corneal transplant in 1314 at Farabi Hospital, Tehran.
- Dr. Malek Hosseini, in 1993, accomplished the first successful liver transplant in Iran, establishing Shiraz University as a prominent liver transplant center.
- Dr. Hossein Mandegar achieved the first successful heart transplant in July 1993 at Shariati Hospital, Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
- Dr. Iraj Fazel, in 1992, performed the pioneering small bowel transplant at Ayatollah Taleghani Hospital.
- Dr. Nik Eghbalian carried out the first pancreas transplant in April 2006 at Shiraz University, marking another success in the realm of organ transplantation. These endeavors reflect Iran’s significant contributions to the field of transplant medicine.
Nutrient-Rich Diet: Following a transplant, maintaining a nutritious diet is crucial. Incorporate a wide variety of healthy foods into your meals, including plenty of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean sources of protein like poultry and fish, beans, and healthy fats such as olive oil. These choices provide essential nutrients and support overall health.
Sodium Control: Keep your salt intake in check to help manage blood pressure and reduce the risk of fluid retention, which can be especially important post-transplant.
Moderate Alcohol Consumption: Limit alcohol consumption to promote liver health and overall well-being during your recovery.
Medication Considerations: Be cautious about grapefruit and grapefruit juice consumption, as they can interact with certain immunosuppressive drugs known as calcineurin inhibitors. Discuss dietary restrictions with your healthcare team.
Physical Activity: Engage in regular physical activity as part of your recovery plan. Exercise can help you control your weight, strengthen bones, build endurance and muscle, and maintain a healthy heart. Gradually increase your activity level to aid in the healing process.
Cancer Prevention: Take proactive steps to prevent cancer after a transplant. Avoid smoking, use sunscreen when outdoors, and follow your doctor’s recommendations for cancer screenings.
Transplant Goals: Understand that the goals of a bone marrow transplant may vary based on your individual condition but typically include managing or treating the disease, extending your life, and enhancing your overall quality of life.
Adhering to these guidelines can contribute to a successful post-transplant recovery and long-term well-being.
What is organ transplant rejection?
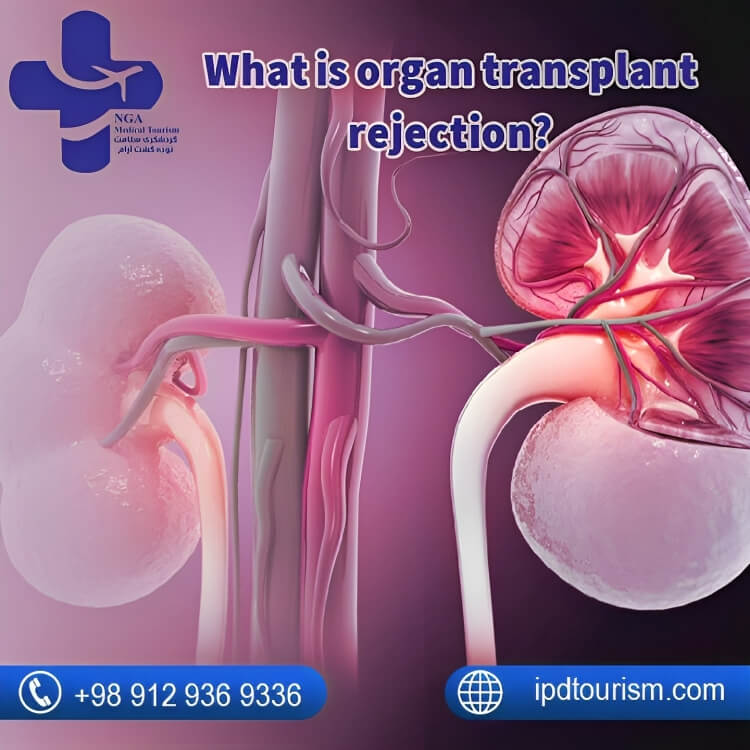
Organ transplantation rejection is a process by which the recipient’s immune system recognizes the transplanted organ as foreign tissue and mounts an immune response against it, potentially leading to the organ’s failure. There are two primary types of rejection: hyperacute rejection, which occurs almost immediately and is often irreversible, and acute rejection, which develops within weeks to months and is treatable with immunosuppressive medications. Chronic rejection can also develop over time, causing gradual damage to the transplanted organ. Preventing rejection involves carefully matching donor and recipient, along with lifelong immunosuppressive therapy to suppress the recipient’s immune response, allowing the transplanted organ to function successfully.
Is organ donation allowed in Iran?
The Iranian Model indeed sets Iran apart in organ transplantation. The prohibition of organ trade, coupled with a focus on voluntary and altruistic donation, reflects a commitment to ethical practices. The government’s active role in regulation and oversight adds an extra layer of assurance. This approach not only addresses the shortage of organs but also emphasizes the importance of ethical considerations in the field of transplantation.
How does organ donation work in Iran?
Iran has an interesting approach to organ donation. It operates on an incentive-based system where the government covers healthcare fees for the donor’s family if organs are donated from a public hospital. This can help alleviate financial burdens on the family during a difficult time and encourages organ donation. It’s a unique way to promote a positive societal impact.
Why choose Iran for Organ Transplantation?

Iran is a notable destination for organ transplantation due to its unique and government-regulated organ donation system. Additionally, Iran boasts a well-established infrastructure for transplantation procedures, experienced medical professionals, and relatively lower costs compared to Western nations. However, it’s crucial to note that the decision to choose Iran for organ transplantation should be made carefully, considering various factors such as the specific medical needs of the patient and potential legal and ethical concerns associated with compensated organ donations. Furthermore, Iran’s commitment to the ethical aspects of organ transplantation is exemplified by its strict regulations that prioritize fair and transparent allocation of organs to recipients, regardless of their financial status or social standing.
Why Choose ipdtourism?
Ipdtourism is the ideal choice for individuals seeking organ transplant-related services in Iran. We specialize in providing comprehensive support and services to patients traveling to Iran for organ transplantation. With a deep understanding of the complexities involved in this critical medical procedure, IPDtourism offers a range of services, including connecting patients with reputable medical institutions and experienced healthcare professionals, facilitating the entire transplantation process, ensuring compliance with legal and ethical standards, and providing assistance with travel logistics and accommodation.
In conclusion, Iran has a remarkable history in the field of organ transplantation, marked by pioneering efforts, government support, and innovative solutions to address the challenges associated with organ shortages. The establishment of regulations, such as the Organ Transplantation Brain Death Act, has helped ensure ethical and transparent practices in organ procurement and transplantation. Iran’s distinctive living donor program, which offers financial compensation to donors while upholding ethical principles, has significantly increased the availability of organs, particularly kidneys, for transplantation. This unique approach has garnered international recognition and has been influential in shaping discussions on organ donation ethics globally. While Iran has made significant strides in organ transplantation, it continues to face ongoing challenges and opportunities for further advancements in this life-saving field.
FAQ
“Iran’s cadaveric kidney donation system is similar to that of many other countries. [16] It is centralised under the Ministry of Health and removal of organs requires either a donor card signed by the deceased or family consent.
Spain has been the acknowledged leader in donations for number of years with 35.3 donors per million. Some of the difference in rates is due to an opt-out versus opt-in policy. In Spain you are considered a donor unless you make the effort to opt out of the donation system.
In the Iranian model of renal transplantation program, regulations have been put in place to prevent transplant tourism. Foreigners are not allowed to undergo renal transplantation from Iranian living-unrelated donors. They also are not permitted to volunteer as kidney donors for Iranian patients.
Results: Iran’s national deceased donation rate from 2002 to 2019 increased 19.06-fold from . 75 to 14.3 per million population (PMP). After the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic, the rate of organ donation in Iran decreased significantly.
In Iran, a legal compensated and regulated living unrelated donor kidney transplant program has been adopted since 1988, in which recipients are matched with liveunrelated donors through the Iran Kidney Foundation and the recipients are compensated dually by the government and the recipient.
- In the United States, the most commonly transplanted organs are the kidney, liver, heart, lungs, pancreas and intestines. …
- In the U.S, the most commonly transplanted tissues are bones, tendons, ligaments, skin, heart valves, blood vessels and corneas.